Rad51-mediated interhomolog recombination during budding yeast meiosis is promoted by the meiotic recombination checkpoint and the conserved Pif1 helicase
- PMID: 36508468
- PMCID: PMC9779700
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010407
Rad51-mediated interhomolog recombination during budding yeast meiosis is promoted by the meiotic recombination checkpoint and the conserved Pif1 helicase
Abstract
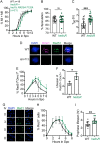
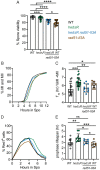
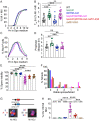
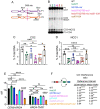
During meiosis, recombination between homologous chromosomes (homologs) generates crossovers that promote proper segregation at the first meiotic division. Recombination is initiated by Spo11-catalyzed DNA double strand breaks (DSBs). 5' end resection of the DSBs creates 3' single strand tails that two recombinases, Rad51 and Dmc1, bind to form presynaptic filaments that search for homology, mediate strand invasion and generate displacement loops (D-loops). D-loop processing then forms crossover and non-crossover recombinants. Meiotic recombination occurs in two temporally distinct phases. During Phase 1, Rad51 is inhibited and Dmc1 mediates the interhomolog recombination that promotes homolog synapsis. In Phase 2, Rad51 becomes active and functions with Rad54 to repair residual DSBs, making increasing use of sister chromatids. The transition from Phase 1 to Phase 2 is controlled by the meiotic recombination checkpoint through the meiosis-specific effector kinase Mek1. This work shows that constitutive activation of Rad51 in Phase 1 results in a subset of DSBs being repaired by a Rad51-mediated interhomolog recombination pathway that is distinct from that of Dmc1. Strand invasion intermediates generated by Rad51 require more time to be processed into recombinants, resulting in a meiotic recombination checkpoint delay in prophase I. Without the checkpoint, Rad51-generated intermediates are more likely to involve a sister chromatid, thereby increasing Meiosis I chromosome nondisjunction. This Rad51 interhomolog recombination pathway is specifically promoted by the conserved 5'-3' helicase PIF1 and its paralog, RRM3 and requires Pif1 helicase activity and its interaction with PCNA. This work demonstrates that (1) inhibition of Rad51 during Phase 1 is important to prevent competition with Dmc1 for DSB repair, (2) Rad51-mediated meiotic recombination intermediates are initially processed differently than those made by Dmc1, and (3) the meiotic recombination checkpoint provides time during prophase 1 for processing of Rad51-generated recombination intermediates.
Copyright: This is an open access article, free of all copyright, and may be freely reproduced, distributed, transmitted, modified, built upon, or otherwise used by anyone for any lawful purpose. The work is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 public domain dedication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Down-regulation of Rad51 activity during meiosis in yeast prevents competition with Dmc1 for repair of double-strand breaks.PLoS Genet. 2014 Jan;10(1):e1004005. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004005. Epub 2014 Jan 23. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 24465215 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic crossover control by concerted action of Rad51-Dmc1 in homolog template bias and robust homeostatic regulation.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(12):e1003978. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003978. Epub 2013 Dec 19. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 24367271 Free PMC article.
-
Mek1 Down Regulates Rad51 Activity during Yeast Meiosis by Phosphorylation of Hed1.PLoS Genet. 2016 Aug 2;12(8):e1006226. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006226. eCollection 2016 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27483004 Free PMC article.
-
The meiotic-specific Mek1 kinase in budding yeast regulates interhomolog recombination and coordinates meiotic progression with double-strand break repair.Curr Genet. 2019 Jun;65(3):631-641. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-00937-3. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 30671596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repair of DNA double-strand breaks in plant meiosis: role of eukaryotic RecA recombinases and their modulators.Plant Reprod. 2023 Mar;36(1):17-41. doi: 10.1007/s00497-022-00443-6. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Plant Reprod. 2023. PMID: 35641832 Review.
Cited by
-
An acidic loop in the forkhead-associated domain of the yeast meiosis-specific kinase Mek1 interacts with a specific motif in a subset of Mek1 substrates.Genetics. 2024 Sep 4;228(1):iyae106. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae106. Genetics. 2024. PMID: 38979911 Free PMC article.
-
Homologous Recombination and Repair Functions Required for Mutagenicity during Yeast Meiosis.Genes (Basel). 2023 Oct 28;14(11):2017. doi: 10.3390/genes14112017. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38002960 Free PMC article.
-
FIGL1 attenuates meiotic interhomolog repair and is counteracted by the RAD51 paralog XRCC2 and the chromosome axis protein ASY1 during meiosis.New Phytol. 2024 Dec;244(6):2442-2457. doi: 10.1111/nph.20181. Epub 2024 Oct 17. New Phytol. 2024. PMID: 39420761 Free PMC article.
-
Premeiotic deletion of Eif2s2 causes oocyte arrest at the early diplotene stage and apoptosis in mice.Cell Prolif. 2024 Dec;57(12):e13718. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13718. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Cell Prolif. 2024. PMID: 39044637 Free PMC article.
-
An acidic loop in the FHA domain of the yeast meiosis-specific kinase Mek1 interacts with a specific motif in a subset of Mek1 substrates.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 25:2024.05.24.595751. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.24.595751. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Genetics. 2024 Sep 4;228(1):iyae106. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae106. PMID: 38826409 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Petronczki M, Siomos MF, Nasmyth K. Un menage a quatre: the molecular biology of chromosome segregation in meiosis. Cell. 2003;112(4):423–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

