Efficacy, Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of MMV390048 in Acute Uncomplicated Malaria
- PMID: 36509063
- PMCID: PMC9833083
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.22-0567
Efficacy, Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of MMV390048 in Acute Uncomplicated Malaria
Abstract
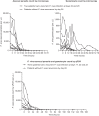
An open label, phase IIa study conducted in Ethiopia evaluated the efficacy, safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of a single 120-mg dose of the phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase inhibitor MMV390048 in Plasmodium vivax malaria. The study was not completed for operational reasons and emerging teratotoxicity data. For the eight adult male patients enrolled, adequate clinical and parasitological response at day 14 (primary endpoint) was 100% (8/8). Asexual parasites and gametocytes were cleared in all patients by 66 and 78 hours postdose, respectively. There were two recurrent P. vivax infections (days 20 and 28) and a new Plasmodium falciparum infection (day 22). MMV390048 exposure in P. vivax patients was lower than previously observed for healthy volunteers. Mild adverse events, mainly headache and gastrointestinal symptoms, were reported by eight patients. Single-dose MMV390048 (120 mg) rapidly cleared asexual parasites and gametocytes in patients with P. vivax malaria and was well tolerated.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02880241.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization , 2021. World malaria report. Available at: https://www.who.int/teams/global-malaria-programme/reports/world-malaria.... Accessed July 11, 2022.
-
- Sternberg AR Roepe PD , 2020. Heterologous expression, purification, and functional analysis of the Plasmodium falciparum phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase iiibeta. Biochemistry 59: 2494–2506. - PubMed
-
- Ghidelli-Disse S et al. 2014. Identification of Plasmodium PI4 kinase as target of MMV390048 by chemoproteomics. Malar J 13 ( Suppl 1 ): 38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical