Designer installation of a substrate recruitment domain to tailor enzyme specificity
- PMID: 36509904
- PMCID: PMC10065947
- DOI: 10.1038/s41589-022-01206-0
Designer installation of a substrate recruitment domain to tailor enzyme specificity
Abstract
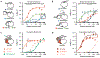
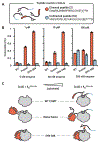
Promiscuous enzymes that modify peptides and proteins are powerful tools for labeling biomolecules; however, directing these modifications to desired substrates can be challenging. Here, we use computational interface design to install a substrate recognition domain adjacent to the active site of a promiscuous enzyme, catechol O-methyltransferase. This design approach effectively decouples substrate recognition from the site of catalysis and promotes modification of peptides recognized by the recruitment domain. We determined the crystal structure of this novel multidomain enzyme, SH3-588, which shows that it closely matches our design. SH3-588 methylates directed peptides with catalytic efficiencies exceeding the wild-type enzyme by over 1,000-fold, whereas peptides lacking the directing recognition sequence do not display enhanced efficiencies. In competition experiments, the designer enzyme preferentially modifies directed substrates over undirected substrates, suggesting that we can use designed recruitment domains to direct post-translational modifications to specific sequence motifs on target proteins in complex multisubstrate environments.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests Statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

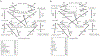


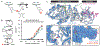

Similar articles
-
Domain interactions in protein tyrosine kinase Csk.Biochemistry. 1999 Aug 24;38(34):11147-55. doi: 10.1021/bi990827+. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10460171
-
Directed evolution of a new catalytic site in 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate aldolase from Escherichia coli.Structure. 2001 Jan 10;9(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00555-4. Structure. 2001. PMID: 11342129
-
Role of the Brk SH3 domain in substrate recognition.Oncogene. 2004 Mar 18;23(12):2216-23. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207339. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 14676834
-
The SH3 domain--a family of versatile peptide- and protein-recognition module.Front Biosci. 2008 May 1;13:4938-52. doi: 10.2741/3053. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 18508559 Review.
-
Promiscuous Enzymes for Residue-Specific Peptide and Protein Late-Stage Functionalization.Chembiochem. 2023 Sep 1;24(17):e202300372. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202300372. Epub 2023 Jul 19. Chembiochem. 2023. PMID: 37338668 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Peptides hit the catalysis walk.Nat Chem Biol. 2023 Apr;19(4):395-396. doi: 10.1038/s41589-022-01210-4. Nat Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 36509905 No abstract available.
-
There's more to enzyme antagonism than inhibition.Bioorg Med Chem. 2023 Mar 15;82:117231. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2023.117231. Epub 2023 Mar 5. Bioorg Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36893527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LICEDB: light industrial core enzyme database for industrial applications and AI enzyme design.Database (Oxford). 2025 Feb 19;2025:baaf001. doi: 10.1093/database/baaf001. Database (Oxford). 2025. PMID: 39980225 Free PMC article.
-
Dissection of the role of a Src homology 3 domain in the evolution of binding preference of paralogous proteins.Genetics. 2024 Jan 3;226(1):iyad175. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyad175. Genetics. 2024. PMID: 37793087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen I, Howarth M, Lin W & Ting AY Site-specific labeling of cell surface proteins with biophysical probes using biotin ligase. Nat Methods 2, 99–104 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Pellicena P, Stowell KR & Miller WT Enhanced phosphorylation of Src family kinase substrates containing SH2 domain binding sites. Journal of Biological Chemistry 273, 15325–15328 (1998). - PubMed
Methods-only References
-
- Lerner C et al. Design of Potent and Druglike Nonphenolic Inhibitors for Catechol O-Methyltransferase Derived from a Fragment Screening Approach Targeting the S-Adenosyl-l-methionine Pocket. J Med Chem 59, 10163–10175 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

