Perceiving distance in virtual reality: theoretical insights from contemporary technologies
- PMID: 36511405
- PMCID: PMC9745869
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2021.0456
Perceiving distance in virtual reality: theoretical insights from contemporary technologies
Abstract
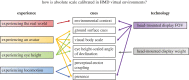
Decades of research have shown that absolute egocentric distance is underestimated in virtual environments (VEs) when compared with the real world. This finding has implications on the use of VEs for applications that require an accurate sense of absolute scale. Fortunately, this underperception of scale can be attenuated by several factors, making perception more similar to (but still not the same as) that of the real world. Here, we examine these factors as two categories: (i) experience inherent to the observer, and (ii) characteristics inherent to the display technology. We analyse how these factors influence the sources of information for absolute distance perception with the goal of understanding how the scale of virtual spaces is calibrated. We identify six types of cues that change with these approaches, contributing both to a theoretical understanding of depth perception in VEs and a call for future research that can benefit from changing technologies. This article is part of the theme issue 'New approaches to 3D vision'.
Keywords: distance perception; virtual reality; visual cues.
Figures


References
-
- Renner RS, Velichkovsky BM, Helmert JR. 2013. The perception of egocentric distances in virtual environments—a review. ACM Comput. Surv. 46, 23:1-23:40. (10.1145/2543581.2543590) - DOI
-
- Creem-Regehr SH, Stefanucci JK, Thompson WB. 2015. Perceiving absolute scale in virtual environments: how theory and application have mutually informed the role of body-based perception. In Psychology of learning and motivation, vol. 62 (ed. BH Ross), pp. 195–224. New York, NY: Academic Press. See http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0079742114000073.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

