Prognostic Significance of Hemoglobin/Prognostic Nutritional Index and Hemoglobin/Red Blood Cell Distribution in Rectal Cancer
- PMID: 36511609
- PMCID: PMC10081009
- DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2022.22203
Prognostic Significance of Hemoglobin/Prognostic Nutritional Index and Hemoglobin/Red Blood Cell Distribution in Rectal Cancer
Abstract
Background: We aimed to investigate the effect of hemoglobin/prognostic nutritional index and hemoglobin/red blood cell distribution, which are indicators of inflammation and nutrition, on prognosis and survival in patients with rectal cancer.
Methods: The retrospective study reviewed medical records of 138 patients with rectal cancer who were followed up between 2010 and 2021. The effects of hemoglobin/red blood cell distribution, hemoglobin/prognostic nutritional index, tumor stage, and lymph node status on survival and prognosis were evaluated using univariate and multivariate analyses. Overall survival and disease-free survival were calculated for both groups.
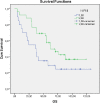
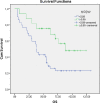
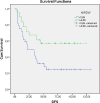
Results: Survival and prognosis were found to be significantly better in nonanemic patients with the hemoglobin/prognostic nutritional index higher than the cut-off value than in anemic patients with a normal or lower hemoglobin/prognostic nutritional index. Similarly, survival and prognosis were found to be significantly better in nonanemic patients with a hemoglobin/red blood cell distribution higher than the cut-off value than in anemic patients with a normal or lower hemoglobin/red blood cell distribution.
Conclusion: The results indicated that nutrition and inflammatory markers have independent prognostic significance in rectal cancer. These markers are simple, inexpensive, and useful biomarkers commonly used in clinical practice, and they were found to predict overall survival and disease-free survival independently.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
