Cardiac MRI in patients with COVID-19 infection
- PMID: 36512043
- PMCID: PMC9745285
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-022-09325-x
Cardiac MRI in patients with COVID-19 infection
Abstract
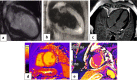
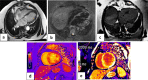
Objective: COVID-19 infection is a systemic disease with various cardiovascular symptoms and complications. Cardiac MRI with late gadolinium enhancement is the modality of choice for the assessment of myocardial involvement. T1 and T2 mapping can increase diagnostic accuracy and improve further management. Our study aimed to evaluate the different aspects of myocardial damage in cases of COVID-19 infection using cardiac MRI.
Methods: This descriptive retrospective study included 86 cases, with a history of COVID-19 infection confirmed by positive RT-PCR, who met the inclusion criteria. Patients had progressive chest pain or dyspnoea with a suspected underlying cardiac cause, either by an abnormal electrocardiogram or elevated troponin levels. Cardiac MRI was performed with late contrast-enhanced (LGE) imaging, followed by T1 and T2 mapping.
Results: Twenty-four patients have elevated hsTnT with a median hsTnT value of 133 ng/L (IQR: 102 to 159 ng/L); normal value < 14 ng/L. Other sixty-two patients showed elevated hsTnI with a median hsTnI value of 1637 ng/L (IQR: 1340 to 2540 ng/L); normal value < 40 ng/L. CMR showed 52 patients with acute myocarditis, 23 with Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, and 11 with myocardial infarction. Invasive coronary angiography was performed only in selected patients.
Conclusion: Different COVID-19-related cardiac injuries may cause similar clinical symptoms. Cardiac MRI is the modality of choice to differentiate between the different types of myocardial injury such as Takotsubo cardiomyopathy and infection-related cardiomyopathy or even acute coronary syndrome secondary to vasculitis or oxygen-demand mismatch.
Key points: • It is essential to detect early COVID-related cardiac injury using different cardiac biomarkers and cardiac imaging, as it has a significant impact on patient management and outcome. • Cardiac MRI is the modality of choice to differentiate between the different aspects of COVID-related myocardial injury.
Keywords: Acute coronary syndrome; Coronavirus; Magnetic resonance imaging; Myocarditis; Takotsubo cardiomyopathy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures




References
-
- Caforio AL, Pankuweit S, Arbustini E, et al. Current state of knowledge on etiology, diagnosis, management, and therapy of myocarditis: a position statement of the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur Heart J. 2013;34:2636–2648. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht210. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

