Outcomes of On-Label Reduced-Dose Edoxaban in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: The LEDIOS Registry
- PMID: 36513051
- PMCID: PMC9745682
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e335
Outcomes of On-Label Reduced-Dose Edoxaban in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: The LEDIOS Registry
Abstract
Background: Non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants (NOACs) are effective in preventing thromboembolisms and reduce the risk of bleeding compared with warfarin. There are few reports on the outcomes of on-label reduced-dose NOACs. The aim of this study was to assess the safety and efficacy of on-label reduced-dose edoxaban in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF).
Methods: This study is a multi-center, prospective, non-interventional study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of on-label reduced-dose edoxaban in patients with AF. We evaluated outcomes of major bleeding, stroke or systemic embolism, all-cause death, and composite clinical outcomes.
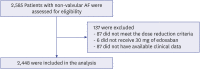
Results: A total of 2,448 patients (mean age 75.0 ± 8.3 years, 801 [32.7%] males) was included in the present study. The mean CHA2DS2-VASc score was 3.7 ± 1.5. Major bleeding events occurred at a rate of 1.34%/yr. The event rate of strokes and systemic embolisms was 1.13%/yr. The overall net clinical outcomes occurred at a rate of 3.19%/yr. There were no significant differences according to the number of dose reduction criteria, renal dysfunction, or body weight. Higher HAS-BLED score and higher combination of CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED score was associated with an increased risk of composite clinical outcomes compared to the lower score groups.
Conclusions: This study was the largest prospective real-world study to investigate the safety and efficacy of on-label low-dose edoxaban in an Asian population. Reduced-dose edoxaban can be used safely in patients with severe renal dysfunction or extremely low body weight. Our observation suggests that physicians should consider bleeding risk even in a low-dose regimen.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03554837.
Keywords: Atrial Fibrillation; Efficacy; Oral Anticoagulants; Reduced Dose; Safety.
© 2022 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose. The funding organization made no influence in the present study.
Figures
References
-
- Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomström-Lundqvist C, et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): the Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(5):373–498. - PubMed
-
- January CT, Wann LS, Calkins H, Chen LY, Cigarroa JE, Cleveland JC, Jr, et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society in Collaboration with the Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Circulation. 2019;140(2):e125–e151. - PubMed
-
- Connolly SJ, Ezekowitz MD, Yusuf S, Eikelboom J, Oldgren J, Parekh A, et al. Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(12):1139–1151. - PubMed
-
- Giugliano RP, Ruff CT, Braunwald E, Murphy SA, Wiviott SD, Halperin JL, et al. Edoxaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(22):2093–2104. - PubMed
-
- Granger CB, Alexander JH, McMurray JJ, Lopes RD, Hylek EM, Hanna M, et al. Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(11):981–992. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical