ASCOT ADAPT study of COVID-19 therapeutics in hospitalised patients: an international multicentre adaptive platform trial
- PMID: 36514143
- PMCID: PMC9747535
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-022-06929-y
ASCOT ADAPT study of COVID-19 therapeutics in hospitalised patients: an international multicentre adaptive platform trial
Abstract
Background: SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with a significant risk of hospitalisation, death, and prolonged impact on quality of life. Evaluation of new treatment options and optimising therapeutic management of people hospitalised with SARS-CoV-2 infection remains essential, but rapid changes in pandemic conditions and potential therapies have limited the utility of traditional approaches to randomised controlled trials.
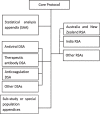
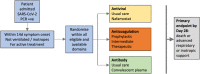
Methods: ASCOT ADAPT is an international, investigator-initiated, adaptive platform, randomised controlled trial of therapeutics for non-critically ill patients hospitalised with COVID-19. The study design is open label and pragmatic. Potential participants are hospitalised adults with PCR confirmed, symptomatic, SARS-CoV-2 infection, within 14 days of symptom onset. Domains include antiviral, antibody and anticoagulant interventions, with a composite primary outcome of 28-day mortality or progression to intensive-care level respiratory or haemodynamic support. Initial interventions include intravenous nafamostat and variable dose anticoagulation. A range of secondary endpoints, and substudies for specific domains and interventions are outlined.
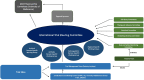
Discussion: This paper presents the trial protocol and management structure, including international governance, remote site monitoring and biobanking activities and provides commentary on ethical and pragmatic considerations in establishing the ASCOT ADAPT trial under pandemic conditions.
Trial registration: Australian and New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry (ACTRN12620000445976) and ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04483960).
Keywords: Antibody; Anticoagulation; Antiviral medication; COVID-19; Randomised controlled trial; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Denholm JT, David J, Paterson D, et al. The Australasian COVID-19 Trial (ASCOT) to assess clinical outcomes in hospitalised patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19) treated with lopinavir/ritonavir and/or hydroxychloroquine compared to standard of care: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2020;21(1):1–3. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04576-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous