Plasma Exchange for the Treatment of Severe Hypertriglyceridemic Pancreatitis With Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Case Report From Sub-Saharan Africa
- PMID: 36514570
- PMCID: PMC9735322
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.31311
Plasma Exchange for the Treatment of Severe Hypertriglyceridemic Pancreatitis With Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Case Report From Sub-Saharan Africa
Abstract
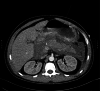
The triad of acute pancreatitis, diabetic ketoacidosis, and hyperlipidemia is exceedingly rare. Case reports describing this uncommon triad have successfully been managed with insulin infusions only. Herein, we highlight the challenges in making this diagnosis and present Sub-Saharan Africa's first experience with therapeutic plasma exchange in the management of hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis associated with diabetic ketoacidosis, which was initially refractory to insulin infusion alone.
Keywords: diabetic ketoacidosis; hypertriglyceridemia; pancreatitis; plasma exchange; severe.
Copyright © 2022, Mongare et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Organ failure and infection of pancreatic necrosis as determinants of mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis. Petrov MS, Shanbhag S, Chakraborty M, Phillips AR, Windsor JA. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:813–820. - PubMed
-
- Clinical assessment of hyperlipidemic pancreatitis. Fortson MR, Freedman SN, Webster PD 3rd. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8540502/ Am J Gastroenterol. 1995;90:2134–2139. - PubMed
-
- Hypertriglyceridemia-induced acute pancreatitis: a prospective, multicenter, international cohort analysis of 716 acute pancreatitis cases. Mosztbacher D, Hanák L, Farkas N, et al. Pancreatology. 2020;20:608–616. - PubMed
-
- Therapeutic plasma exchange for hypertriglyceridemia induced pancreatitis: a rapid and practical approach. Gavva C, Sarode R, Agrawal D, Burner J. Transfus Apher Sci. 2016;54:99–102. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources