Monitoring PD-L1 Expression on Circulating Tumor-Associated Cells in Recurrent Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma Predicts Response to Immunotherapy With Radiation Therapy
- PMID: 36516370
- PMCID: PMC10166406
- DOI: 10.1200/PO.22.00457
Monitoring PD-L1 Expression on Circulating Tumor-Associated Cells in Recurrent Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma Predicts Response to Immunotherapy With Radiation Therapy
Abstract
Purpose: Current diagnostic methods to determine programmed death 1 (PD-1) receptor and its ligand (PD-L1)/PD-1 immunotherapy (immune checkpoint inhibitor [ICI]) efficacy in recurrent or metastatic non-small-cell lung carcinoma (rmNSCLC) are imprecise. Although previously shown that patients with high tumor PD-L1 (≥ 50%) demonstrate clinical benefit in the form of disease reduction and improved survival, patients with low PD-L1 (< 50%) sometimes benefit from treatment. Since the PD-L1/PD-1 pathway is dynamic, monitoring PD-L1 levels during treatment may be more accurate than a static baseline tumor biopsy; however, rebiopsying the primary or metastatic disease is rarely feasible. Liquid biopsies that measure the upregulation of PD-L1 on tumor-associated cells (TACs), ie, cancer-associated macrophage-like cells and circulating tumor cells, have been performed, but their predictive value for ICI therapy efficacy is unknown.
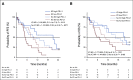
Materials and methods: We initiated a single-blind prospective study to evaluate TAC PD-L1 expression changes in rmNSCLC from blood samples before (T0) and after (T1) treatment with ICI (ICI, n = 41) or without ICI (no ICI, n = 41). Anonymized blood was filtered to isolate TACs, which were then quantified for high/low PD-L1 expression. Progression-free survival (PFS) or overall survival (OS) hazard ratios (HRs) were evaluated at 18 and 24 months by censored univariate analysis.
Results: Increased TAC PD-L1 expression between T0 and T1 in patients who were not treated with ICI had no relationship with PFS or OS. However, increased TAC PD-L1 expression between T0 and T1 in patients treated with ICI had significantly better PFS (HR, 3.49; 95% CI, 1.5 to 8.3; P = .0091) and OS (HR, 3.058; 95% CI, 1.2 to 7.9; P = .0410).
Conclusion: Blood-based monitoring of dynamic changes in PD-L1 in TACs appears to identify patients with rmNSCLC who may benefit from ICI.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures

References
-
- Herbst RS, Baas P, Kim DW, et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;387:1540–1550. - PubMed
-
- Reck M, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG, et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1823–1833. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

