Retinal hemorrhages in abusive head trauma with atraumatic neuroimaging
- PMID: 36516943
- PMCID: PMC9975066
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaapos.2022.10.005
Retinal hemorrhages in abusive head trauma with atraumatic neuroimaging
Abstract
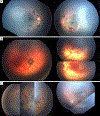
We report 3 cases of suspected abusive head trauma with retinal hemorrhages on fundus examination and neuroimaging findings not necessarily suggestive of shaking injury. Previous studies have suggested that retinal hemorrhages are rare in patients without neuroimaging abnormalities. These cases demonstrate some common features (rib fractures, developmental delay, and history of abuse) that may increase suspicion for abusive head trauma. Our findings suggest a potential role for ophthalmic consultation in scenarios with high clinical suspicion for abusive head trauma without definitive neuroimaging evidence of head injury. The nonspecific neuroimaging features of these 3 cases highlight the importance of interpreting cases with global clinical context.
Copyright © 2022 American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Morad Y, Kim YM, Armstrong DC, Huyer D, Mian M, Levin AV. Correlation between retinal abnormalities and intracranial abnormalities in the shaken baby syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol 2002;134:354–9. - PubMed
-
- Ip SS, Zafar S, Liu TYA, et al. Nonaccidental trauma in pediatric patients: evidence-based screening criteria for ophthalmologic examination. J AAPOS 2020;24:226.e1–5. - PubMed
-
- Thackeray JD, Scribano PV, Lindberg DM. Yield of retinal examination in suspected physical abuse with normal neuroimaging. Pediatrics 2010;125:e1066–71. - PubMed
-
- Greiner MV, Berger RP, Thackeray JD, Lindberg DM. Examining Siblings to Recognize Abuse (ExSTRA) investigators: dedicated retinal examination in children evaluated for physical abuse without radiographically identified traumatic brain injury. J Pediatr 2013;163:527–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

