Maternal Undernutrition Induces Cell Signalling and Metabolic Dysfunction in Undifferentiated Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- PMID: 36517693
- PMCID: PMC10070223
- DOI: 10.1007/s12015-022-10490-1
Maternal Undernutrition Induces Cell Signalling and Metabolic Dysfunction in Undifferentiated Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
Abstract
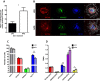
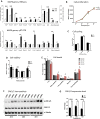
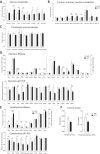
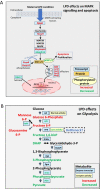
Peri-conceptional environment can induce permanent changes in embryo phenotype which alter development and associate with later disease susceptibility. Thus, mouse maternal low protein diet (LPD) fed exclusively during preimplantation is sufficient to lead to cardiovascular, metabolic and neurological dysfunction in adult offspring. Embryonic stem cell (ESC) lines were generated from LPD and control NPD C57BL/6 blastocysts and characterised by transcriptomics, metabolomics, bioinformatics and molecular/cellular studies to assess early potential mechanisms in dietary environmental programming. Previously, we showed these lines retain cellular and epigenetic characteristics of LPD and NPD embryos after several passages. Here, three main changes were identified in LPD ESC lines. First, their derivation capacity was reduced but pluripotency marker expression was similar to controls. Second, LPD lines had impaired Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway with altered gene expression of several regulators (e.g., Maff, Rassf1, JunD), reduced ERK1/2 signalling capacity and poorer cell survival characteristics which may contribute to reduced derivation. Third, LPD lines had impaired glucose metabolism comprising reduced upstream enzyme expression (e.g., Gpi, Mpi) and accumulation of metabolites (e.g., glucose-6-P, fructose-6-P) above the phosphofructokinase (PFK) gateway with PFK enzyme activity reduced. ESC lines may therefore permit investigation of peri-conceptional programming mechanisms with reduced need for animal experimentation.
Keywords: Cell signalling; DOHaD; Glucose metabolism; MAPK pathway; Maternal low protein diet; Metabolomics; Mouse ES cells; RNAseq.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting or competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

