Recommendations for Early and Comprehensive Management of Type 2 Diabetes and Its Related Cardio-Renal Complications
- PMID: 36517708
- PMCID: PMC9880119
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-022-01340-x
Recommendations for Early and Comprehensive Management of Type 2 Diabetes and Its Related Cardio-Renal Complications
Abstract
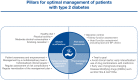
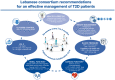
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a global health problem accompanied by an elevated risk of complications, the most common being cardiac and renal diseases. In Lebanon, the prevalence of T2D is estimated at 8-13%. Local medical practice generally suffers from clinical inertia, with gaps in the yearly assessment of clinical manifestations and suboptimal screening for major complications. The joint statement presented here, endorsed by five Lebanese scientific medical societies, aims at providing physicians in Lebanon with a tool for early, effective, and comprehensive care of patients with T2D. Findings from major randomized clinical trials of antidiabetic medications with cardio-renal benefits are presented, together with recommendations from international medical societies. Optimal care should be multidisciplinary and should include a multifactorial risk assessment, lifestyle modifications, and a regular evaluation of risks, including the risks for cardiovascular (CV) and renal complications. With international guidelines supporting a shift in T2D management from glucose-lowering agents to disease-modifying drugs, the present statement recommends treatment initiation with metformin, followed by the addition of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors or glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists due to their CV and renal protection properties, whenever possible. In addition to the selection of the most appropriate pharmacological therapy, efforts should be made to provide continuous education to patients about their disease, with the aim to achieve a patient-centered approach and to foster self-management and adherence to the medical plan. Increasing the level of patient engagement is expected to be associated with favorable health outcomes. Finally, this statement recommends setting an achievable individualized management plan and conducting regular follow-ups to monitor the patients' glycemic status and assess their risks every 3-6 months.
Keywords: Cardiovascular risk; Chronic kidney disease; Diabetic complications; Early management; Glycemic control; Nephropathy risk; Treatment; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures

References
-
- International Diabetes Federation (IDF). Diabetes facts and figures. IDF diabetes atlas, 10th edn. Brussels: IDF; 2021.
-
- Bou-Orm I, Adib S. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of diabetes mellitus in Lebanon: a national survey. East Mediterr Health J. 2020;26(2):182–188. - PubMed
-
- International Diabetes Federation (IDF). Lebanon updates. IDF MENA Members 2020. 2020. https://idf.org/our-network/regions-members/middle-east-and-north-africa.... Accessed 8 Nov 2021.
-
- World Health Association (WHO). Diabetes key facts. Diabetes fact sheets. 2021. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes. Accessed 8 Nov 2021.
-
- Birekland K, Bodegard J, Thuresson M, et al. Cardiorenal disease is the most common first CV manifestation in type 2 diabetes and associated with increased mortality: a large multinational observational study. Diabetes. 2019;68(Supplemet 1).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

