Prolonged hypernutrition impairs TREM2-dependent efferocytosis to license chronic liver inflammation and NASH development
- PMID: 36521495
- PMCID: PMC9839616
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.11.013
Prolonged hypernutrition impairs TREM2-dependent efferocytosis to license chronic liver inflammation and NASH development
Abstract
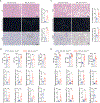
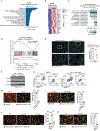
Obesity-induced chronic liver inflammation is a hallmark of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)-an aggressive form of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. However, it remains unclear how such a low-grade, yet persistent, inflammation is sustained in the liver. Here, we show that the macrophage phagocytic receptor TREM2, induced by hepatocyte-derived sphingosine-1-phosphate, was required for efferocytosis of lipid-laden apoptotic hepatocytes and thereby maintained liver immune homeostasis. However, prolonged hypernutrition led to the production of proinflammatory cytokines TNF and IL-1β in the liver to induce TREM2 shedding through ADAM17-dependent proteolytic cleavage. Loss of TREM2 resulted in aberrant accumulation of dying hepatocytes, thereby further augmenting proinflammatory cytokine production. This ultimately precipitated a vicious cycle that licensed chronic inflammation to drive simple steatosis transition to NASH. Therefore, impaired macrophage efferocytosis is a previously unrecognized key pathogenic event that enables chronic liver inflammation in obesity. Blocking TREM2 cleavage to restore efferocytosis may represent an effective strategy to treat NASH.
Keywords: TREM2; chronic inflammation; efferocytosis; nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; proinflammatory cytokines.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Comment in
-
Eating macrophages for a healthy anti-NASH meal.Immunity. 2023 Jan 10;56(1):3-5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.12.011. Immunity. 2023. PMID: 36630915 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

