A panel of blood biomarkers unique to sudden cardiac arrest
- PMID: 36521734
- PMCID: PMC9974970
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2022.12.014
A panel of blood biomarkers unique to sudden cardiac arrest
Abstract
Background: The identification of circulating biomarkers specific for sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) could enhance risk prediction. Of particular interest are biomarkers specific to SCA, independent of coronary artery disease (CAD).
Objective: The purpose of this study was to identify biomarkers of SCA obtained close to the SCA event.
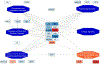
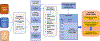
Methods: Twenty cases (survivors of SCA) and 40 age- and sex-matched controls were compared, with a replication analysis of 29 cases matched to 57 controls. A secondary analysis compared 20 SCA cases to 20 controls with CAD. Blood samples were obtained from SCA survivors at a median of 11 months after the SCA event. Proteins were analyzed on a mass spectrometer using data-independent acquisition; a subset of cytokines were analyzed using immunoassays; and 1153 lipids (13 classes) were analyzed. A false discovery rate P value of <.05 identified associated proteins.
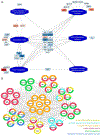
Results: Patients had a mean age of 58 years (range 25-87 years), and 70% were male. A total of 26 protein biomarkers associated with SCA when cases were compared with controls, of which 20 differentiated SCA from CAD. The replication analysis identified 8 of 26 biomarkers, of which 6 were not overlapping with CAD. The top identified biological processes involved the extracellular matrix, coagulation cascades, and platelet activation. Lipids in the lysophosphatidylcholine class were implicated in SCA through the CAD pathway.
Conclusion: We identified a panel of novel blood biomarkers specifically associated with SCA, including several that may be involved outside the CAD pathway. These biomarkers could have mechanistic significance and the potential to enhance clinical prediction of SCA.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cardiac arrest; Death; Prediction; Prevention; Proteomics; Risk stratification; Sudden cardiac.
Copyright © 2022 Heart Rhythm Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
All authors state explicitly that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Syncope and risk of sudden cardiac arrest in coronary artery disease.Int J Cardiol. 2017 Mar 15;231:26-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.12.021. Epub 2016 Dec 12. Int J Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 27988060 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between Sleep Apnea and Coronary Artery Disease on the Incidence of Sudden Cardiac Arrest: A Multi-Center Case-Control Study.Yonsei Med J. 2023 Jan;64(1):48-53. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2022.0417. Yonsei Med J. 2023. PMID: 36579379 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of P-wave morphology in patients with coronary artery disease.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2019 Oct;30(10):2051-2060. doi: 10.1111/jce.14066. Epub 2019 Jul 25. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2019. PMID: 31310355
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus and the risk of sudden cardiac arrest in the community.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2010 Mar;11(1):53-9. doi: 10.1007/s11154-010-9133-5. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2010. PMID: 20195771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Concealed cardiomyopathy" as a cause of previously unexplained sudden cardiac arrest.Int J Cardiol. 2021 Feb 1;324:96-101. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.09.031. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Int J Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 32931854 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploratory study of serum protein biomarkers for sudden cardiac arrest using protein extension assay: A case-control study.PLoS One. 2025 Feb 24;20(2):e0319466. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319466. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39992996 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Sudden Cardiac Death: Looking Beyond Ejection Fraction.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2023 Jun;25(6):525-534. doi: 10.1007/s11886-023-01871-0. Epub 2023 Apr 10. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37036554 Review.
-
Ventricular fibrillation and the proteome problem: can we solve it?Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2024 Mar 11;13(3):273-274. doi: 10.1093/ehjacc/zuad148. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2024. PMID: 38038354 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Chugh SS, Jui J, Gunson K, et al. Current burden of sudden cardiac death: multiple source surveillance versus retrospective death certificate-based review in a large U.S. community. Journal of the American College of Cardiology Sep 15 2004;44:1268–1275. - PubMed
-
- Myerburg RJ, Junttila MJ. Sudden cardiac death caused by coronary heart disease. Circulation Feb 28 2012;125:1043–1052. - PubMed
-
- Albert CM, Ma J, Rifai N, Stampfer MJ, Ridker PM. Prospective study of C-reactive protein, homocysteine, and plasma lipid levels as predictors of sudden cardiac death. Circulation Jun 4 2002;105:2595–2599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

