Multicenter epidemiological investigation and genetic characterization of respiratory syncytial virus and metapneumovirus infections in the pre-pandemic 2018-2019 season in northern and central Italy
- PMID: 36522554
- PMCID: PMC9754777
- DOI: 10.1007/s10238-022-00973-3
Multicenter epidemiological investigation and genetic characterization of respiratory syncytial virus and metapneumovirus infections in the pre-pandemic 2018-2019 season in northern and central Italy
Abstract
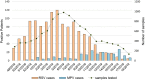
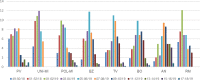
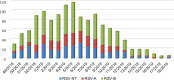
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and human metapneumovirus (HMPV) cause a high burden of disease, particularly in children and the elderly. With the aim to add knowledge on RSV and HMPV infections in Italy, a prospective, multicenter study was conducted by eight centers of the Working Group on Respiratory Virus Infections (GLIViRe), from December 2018-April 2019. Weekly distribution and patients' demographic and clinical data were compared in 1300 RSV and 222 HMPV-positive cases. Phylogenetic analysis of the G-glycoprotein coding region was performed to characterize circulating strains. RSV positivity ranged from 6.4% in outpatients of all ages to 31.7% in hospitalized children; HMPV positivity was 4-1.2% with no age-association. RSV season peaked in February and ended in mid-April: HMPV circulation was higher when RSV decreased in early spring. RSV was more frequent in infants, whereas HMPV infected comparatively more elderly adults; despite, their clinical course was similar. RSV-B cases were two-thirds of the total and had similar clinical severity compared to RSV-A. Phylogenetic analysis showed the circulation of RSV-A ON1 variants and the predominance of RSV-B genotype BA10. HMPV genotype A2c was the prevalent one and presented insertions of different lengths in G. This first multicenter Italian report on seasonality, age-specific distribution, and clinical presentation of RSV and HMPV demonstrated their substantial disease burden in young patients but also in the elderly. These data may provide the basis for a national respiratory virus surveillance network.
Keywords: Bronchiolitis; Human metapneumovirus; Molecular epidemiology; Pneumonia; Respiratory syncytial virus; Respiratory viruses.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Li Y, Wang X, Blau DM, et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in children younger than 5 years in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet. 2022;399:2047–2064. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00478-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

