Association between haematological values and heat shock protein 70 of sickle cell disease patients in Ado-Ekiti, Ekiti State, Nigeria
- PMID: 36523286
- PMCID: PMC9733451
- DOI: 10.11604/pamj.2022.43.47.33346
Association between haematological values and heat shock protein 70 of sickle cell disease patients in Ado-Ekiti, Ekiti State, Nigeria
Abstract
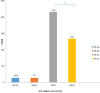
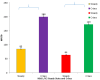
Sickle cell disease, a genetically inherited blood disorder is a major cause of mortality and morbidity in Nigeria. This condition has significant pathological consequences that result in hemolytic events, induction of inflammatory process, vaso-occlusive episodes, and the stress response that leads to the induction of heat shock protein (HSP) 70. Therefore, this study aimed at correlating the level of serum heat shock protein 70 to haematological parameters in sickle cell subjects. A total of eighty-eight (88) consented participants were recruited for this study, which included apparently healthy persons with homozygous hemoglobin (HbAA 20), heterozygous hemoglobin (HbAS 30), homozygous hemoglobin (HbSS 30), and homozygous hemoglobin (HbSC 08). Subjects are in crisis and steady state. Venous blood samples (5 mls) were collected from subjects in ethylene diamine tetra acetic acid (EDTA) container and analyzed hemoglobin variants using hemoglobin electrophoresis, HSP 70 by Elisa method, and full blood count using standard methods. We demonstrated a significant increase (P<005) in HSP 70 levels of sickle cell disease HbSS and HbSC in steady state and crises when compared to the controls HbAA and HbAS. A significant (p<0.0001) increase noticed in the crisis state is higher than in the steady state. While the mean value of mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) (35.1±43.4), pack cell volume (PCV) (22.4±2.7), hemoglobin (Hb) (8.8±0.9), absolute neutrophil count (386.4±31) and Absolute neutrophil count (7.0±2.1) in steady state subjects was significantly higher (p<0.01), as compared to crisis state (29.5±2.5, 21.8±3.4, 7.3±1.8, 269.5±42 and 6.5±2.5) for the respective parameters, whereas, mean corpuscular volume (30.5±3.1), white blood cell (16.8±3.4), absolute lymphocyte count (5.0±1.3) in sickle cell disease subject in crisis state are significantly higher (p<0.01) than in steady state (29.3±2.2, 11.3±2.8, 4.3±1.1) respectively. The mean value of mean corpuscular volume (87.3±8.2) in the crisis state was higher when compared to the steady state (83.5±7.2) and the mean value of red bloood cell (2.7±0.4) in the steady state was higher when compared to the crisis state (2.3±0.7). The differences were not significant (p<0.01). These findings suggest that an association exists between Hsp 70 and haematological parameters in sickle cell subjects. This implies that Hsp 70 might be a marker in oxidative stress, hypoxia, vaso-occlusion crisis, and increased serum Hsp 70 levels seem to reflect systemic inflammation. However, further studies are required to determine whether circulating Hsp 70 plays a causative role in the pathogenesis of sickle cell.
Keywords: Sickle cell disease; haematological parameter; heat shock protein 70.
Copyright: Ayodeji Olusola Dickson Olayanju et al.
Figures
References
-
- Brunetta DM, De Santis GC, Silva-Pinto AC, Oliveira de Oliveira LC, Covas DT. Hydroxyurea increases plasma concentrations of microparticles and reduces coagulation activation and fibrinolysis in patients with sickle cell anemia. Acta Haematol. 2015;133(3):287–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical