Gastric emphysema after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy placement
- PMID: 36524266
- PMCID: PMC9748951
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2022-253374
Gastric emphysema after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy placement
Abstract
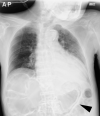
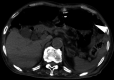
Emphysematous gastritis and gastric emphysema are different diseases. Sometimes, we treat the diseases without distinguishing them clearly because both are rare, and the mortality rate of emphysematous gastritis cases is high (55%). Gastric emphysema is more well known than is emphysematous gastritis after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) placement (80%). Particularly, it is a self-healing disease, and treatment with antibiotics is not required. CT is commonly used to diagnose emphysematous gastritis and gastric emphysema. The amount of radiation exposure is a concern for performing multiple CTs following air disappearance in the gastric wall. Here, we report the case of a 92-year-old man with gastric emphysema after PEG. It was useful to follow-up the patient by performing radiographic examination, and the disease was managed conservatively without antibiotic administration. We report that distinguishing gastric emphysema from emphysematous gastritis was necessary. Moreover, performance excessive tests and treatments should be avoided.
Keywords: Air leaks; Endoscopy; Gas/Free Gas; Stomach and duodenum.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2022. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
