Osteopontin (OPN)/SPP1: from its biochemistry to biological functions in the innate immune system and the central nervous system (CNS)
- PMID: 36525591
- PMCID: PMC10071791
- DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxac060
Osteopontin (OPN)/SPP1: from its biochemistry to biological functions in the innate immune system and the central nervous system (CNS)
Abstract
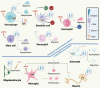
Osteopontin (OPN) is a multifunctional protein, initially identified in osteosarcoma cells with its role of mediating osteoblast adhesion. Later studies revealed that OPN is associated with many inflammatory conditions caused by infections, allergic responses, autoimmunity and tissue damage. Many cell types in the peripheral immune system express OPN with various functions, which could be beneficial or detrimental. Also, more recent studies demonstrated that OPN is highly expressed in the central nervous system (CNS), particularly in microglia during CNS diseases and development. However, understanding of mechanisms underlying OPN's functions in the CNS is still limited. In this review, we focus on peripheral myeloid cells and CNS-resident cells to discuss the expression and functions of OPN.
Keywords: SPP1; innate immunity; intracellular osteopontin (iOPN); myeloid cells; secreted osteopontin (sOPN).
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Japanese Society for Immunology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

