Postoperative Adjuvant Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy With FOLFOX in Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Microvascular Invasion: A Multicenter, Phase III, Randomized Study
- PMID: 36525610
- PMCID: PMC10082249
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.22.01142
Postoperative Adjuvant Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy With FOLFOX in Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Microvascular Invasion: A Multicenter, Phase III, Randomized Study
Abstract
Purpose: To report the efficacy and safety of postoperative adjuvant hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) with 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with microvascular invasion (MVI).
Patients and methods: In this randomized, open-label, multicenter trial, histologically confirmed HCC patients with MVI were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive adjuvant FOLFOX-HAIC (treatment group) or routine follow-up (control group). The primary end point was disease-free survival (DFS) by intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis while secondary end points were overall survival, recurrence rate, and safety.
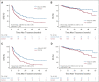
Results: Between June 2016 and August 2021, a total of 315 patients (ITT population) at five centers were randomly assigned to the treatment group (n = 157) or the control group (n = 158). In the ITT population, the median DFS was 20.3 months (95% CI, 10.4 to 30.3) in the treatment group versus 10.0 months (95% CI, 6.8 to 13.2) in the control group (hazard ratio, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.43 to 0.81; P = .001). The overall survival rates at 1 year, 2 years, and 3 years were 93.8% (95% CI, 89.8 to 98.1), 86.4% (95% CI, 80.0 to 93.2), and 80.4% (95% CI, 71.9 to 89.9) for the treatment group and 92.0% (95% CI, 87.6 to 96.7), 86.0% (95% CI, 79.9 to 92.6), and 74.9% (95% CI, 65.5 to 85.7) for the control group (hazard ratio, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.36 to 1.14; P = .130), respectively. The recurrence rates were 40.1% (63/157) in the treatment group and 55.7% (88/158) in the control group. Majority of the adverse events were grade 0-1 (83.8%), with no treatment-related death in both groups.
Conclusion: Postoperative adjuvant HAIC with FOLFOX significantly improved the DFS benefits with acceptable toxicities in HCC patients with MVI.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03192618.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures


References
-
- Hsu SJ, Xu X, Chen MP, et al. : Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with modified FOLFOX as an alternative treatment option in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients with failed or unsuitability for transarterial chemoembolization. Acad Radiol 28:S157-S166, 2021. (Suppl 1) - PubMed
-
- Rodríguez-Perálvarez M, Luong TV, Andreana L, et al. : A systematic review of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma: Diagnostic and prognostic variability. Ann Surg Oncol 20:325-339, 2013 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

