Neuraminidase is a host-directed approach to regulate neutrophil responses in sepsis and COVID-19
- PMID: 36526272
- PMCID: PMC9877938
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.16013
Neuraminidase is a host-directed approach to regulate neutrophil responses in sepsis and COVID-19
Abstract
Background and purpose: Neutrophil overstimulation plays a crucial role in tissue damage during severe infections. Because pathogen-derived neuraminidase (NEU) stimulates neutrophils, we investigated whether host NEU can be targeted to regulate the neutrophil dysregulation observed in severe infections.
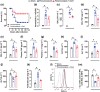
Experimental approach: The effects of NEU inhibitors on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated neutrophils from healthy donors or COVID-19 patients were determined by evaluating the shedding of surface sialic acids, cell activation, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Re-analysis of single-cell RNA sequencing of respiratory tract samples from COVID-19 patients also was carried out. The effects of oseltamivir on sepsis and betacoronavirus-induced acute lung injury were evaluated in murine models.
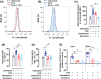
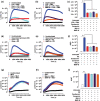
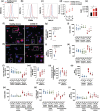
Key results: Oseltamivir and zanamivir constrained host NEU activity, surface sialic acid release, cell activation, and ROS production by LPS-activated human neutrophils. Mechanistically, LPS increased the interaction of NEU1 with matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9). Inhibition of MMP-9 prevented LPS-induced NEU activity and neutrophil response. In vivo, treatment with oseltamivir fine-tuned neutrophil migration and improved infection control as well as host survival in peritonitis and pneumonia sepsis. NEU1 also is highly expressed in neutrophils from COVID-19 patients, and treatment of whole-blood samples from these patients with either oseltamivir or zanamivir reduced neutrophil overactivation. Oseltamivir treatment of intranasally infected mice with the mouse hepatitis coronavirus 3 (MHV-3) decreased lung neutrophil infiltration, viral load, and tissue damage.
Conclusion and implications: These findings suggest that interplay of NEU1-MMP-9 induces neutrophil overactivation. In vivo, NEU may serve as a host-directed target to dampen neutrophil dysfunction during severe infections.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; metalloproteinase-9; neuraminidase; neutrophil; oseltamivir; sepsis; sialic acid; zanamivir.
© 2022 British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures




References
-
- Abdulkhalek, S. , Amith, S. R. , Franchuk, S. L. , Jayanth, P. , Guo, M. , Finlay, T. , Gilmour, A. , Guzzo, C. , Gee, K. , Beyaert, R. , & Szewczuk, M. R. (2011). Neu1 sialidase and matrix metalloproteinase‐9 cross‐talk is essential for toll‐like receptor activation and cellular signaling. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286(42), 36532–36549. 10.1074/jbc.M111.237578 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alexander, S. P. , Cosentino, B. J. , Schooley, R. L. , Mathie, A. , Peters, J. A. , Veale, E. L. , Armstrong, J. F. , Faccenda, E. , Harding, S. D. , Pawson, A. J. , Southan, C. , Davies, J. A. , Annett, S. , Boison, D. , Burns, K. E. , Dessauer, C. , Gertsch, J. , Helsby, N. A. , Izzo, A. A. , … Wong, S. S. (2021). The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2021/22: Enzymes. British Journal of Pharmacology, 178(Suppl 1), S313–S411. 10.1111/bph.15542 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Amith, S. R. , Jayanth, P. , Franchuk, S. , Finlay, T. , Seyrantepe, V. , Beyaert, R. , Pshezhetsky, A. V. , & Szewczuk, M. R. (2010). Neu1 desialylation of sialyl α‐2,3‐linked β‐galactosyl residues of TOLL‐like receptor 4 is essential for receptor activation and cellular signaling. Cellular Signaling, 22, 314–324. 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.09.038 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Amith, S. R. , Jayanth, P. , Franchuk, S. , Siddiqui, S. , Seyrantepe, V. , Gee, K. , Basta, S. , Beyaert, R. , Pshezhetsky, A. V. , & Szewczuk, M. R. (2009). Dependence of pathogen molecule‐induced toll‐like receptor activation and cell function on Neu1 sialidase. Glycoconjugate Journal, 26, 1197–1212. 10.1007/s10719-009-9239-8 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

