Consistency of preferred retinal locus across tasks and participants trained with a simulated scotoma
- PMID: 36527839
- PMCID: PMC9914520
- DOI: 10.1016/j.visres.2022.108158
Consistency of preferred retinal locus across tasks and participants trained with a simulated scotoma
Abstract
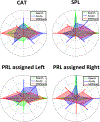
After loss of central vision following retinal pathologies such as macular degeneration (MD), patients often adopt compensatory strategies including developing a "preferred retinal locus" (PRL) to replace the fovea in tasks involving fixation. A key question is whether patients develop multi-purpose PRLs or whether their oculomotor strategies adapt to the demands of the task. While most MD patients develop a PRL, clinical evidence suggests that patients may develop multiple PRLs and switch between them according to the task at hand. To understand this, we examined a model of central vision loss in normally seeing individuals and tested whether they used the same or different PRLs across tasks after training. Nineteen participants trained for 10 sessions on contrast detection while in conditions of gaze-contingent, simulated central vision loss. Before and after training, peripheral looking strategies were evaluated during tasks measuring visual acuity, reading abilities and visual search. To quantify strategies in these disparate, naturalistic tasks, we measured and compared the amount of task-relevant information at each of 8 equally spaced, peripheral locations, while participants performed the tasks. Results showed that some participants used consistent viewing strategies across tasks whereas other participants' strategies differed depending on task. This novel method allows quantification of peripheral vision use even in relatively ecological tasks. These results represent one of the first examinations of peripheral viewing strategies across tasks in simulated vision loss. Results suggest that individual differences in peripheral looking strategies following simulated central vision loss may model those developed in pathological vision loss.
Keywords: Central vision loss; Eye movements; Macular Degeneration; Peripheral vision.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures