A solution structure analysis reveals a bent collagen triple helix in the complement activation recognition molecule mannan-binding lectin
- PMID: 36528062
- PMCID: PMC9898670
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102799
A solution structure analysis reveals a bent collagen triple helix in the complement activation recognition molecule mannan-binding lectin
Abstract
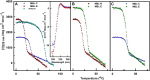
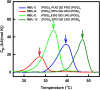
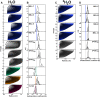
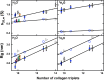
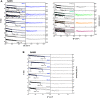
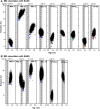
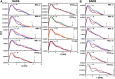
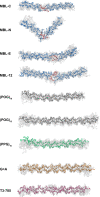
Collagen triple helices are critical in the function of mannan-binding lectin (MBL), an oligomeric recognition molecule in complement activation. The MBL collagen regions form complexes with the serine proteases MASP-1 and MASP-2 in order to activate complement, and mutations lead to common immunodeficiencies. To evaluate their structure-function properties, we studied the solution structures of four MBL-like collagen peptides. The thermal stability of the MBL collagen region was much reduced by the presence of a GQG interruption in the typical (X-Y-Gly)n repeat compared to controls. Experimental solution structural data were collected using analytical ultracentrifugation and small angle X-ray and neutron scattering. As controls, we included two standard Pro-Hyp-Gly collagen peptides (POG)10-13, as well as three more peptides with diverse (X-Y-Gly)n sequences that represented other collagen features. These data were quantitatively compared with atomistic linear collagen models derived from crystal structures and 12,000 conformations obtained from molecular dynamics simulations. All four MBL peptides were bent to varying degrees up to 85o in the best-fit molecular dynamics models. The best-fit benchmark peptides (POG)n were more linear but exhibited a degree of conformational flexibility. The remaining three peptides showed mostly linear solution structures. In conclusion, the collagen helix is not strictly linear, the degree of flexibility in the triple helix depends on its sequence, and the triple helix with the GQG interruption showed a pronounced bend. The bend in MBL GQG peptides resembles the bend in the collagen of complement C1q and may be key for lectin pathway activation.
Keywords: analytical ultracentrifugation; atomistic modeling; collagen; complement; molecular dynamics; small-angle X-ray scattering; small-angle neutron scattering.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Non-linearity of the collagen triple helix in solution and implications for collagen function.Biochem J. 2017 Jun 16;474(13):2203-2217. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170217. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 28533266 Free PMC article.
-
Near-planar solution structures of mannose-binding lectin oligomers provide insight on activation of lectin pathway of complement.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 3;287(6):3930-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.320341. Epub 2011 Dec 13. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22167201 Free PMC article.
-
Location of MBL-associated serine proteases binding motifs on human mannan-binding lectin (MBL).Protein Pept Lett. 2010 Jan;17(1):131-6. doi: 10.2174/092986610789909566. Protein Pept Lett. 2010. PMID: 20214636
-
Biochemistry and genetics of mannan-binding lectin (MBL).Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Aug;31(Pt 4):748-52. doi: 10.1042/bst0310748. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003. PMID: 12887296 Review.
-
Complement activating soluble pattern recognition molecules with collagen-like regions, mannan-binding lectin, ficolins and associated proteins.Mol Immunol. 2007 Sep;44(16):3875-88. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.06.005. Mol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17768106 Review.
Cited by
-
The solution structure of the heavy chain-only C5-Fc nanobody reveals exposed variable regions that are optimal for COVID-19 antigen interactions.J Biol Chem. 2023 Nov;299(11):105337. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105337. Epub 2023 Oct 12. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37838175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ramachandran G.N., Kartha G. Structure of collagen. Nature. 1954;174:269–270. - PubMed
-
- Rich A., Crick F.H. The molecular structure of collagen. J. Mol. Biol. 1961;3:483–506. - PubMed
-
- Bella J. Collagen structure: new tricks from a very old dog. Biochem. J. 2016;473:1001–1025. - PubMed
-
- Domene C., Jorgensen C., Abbasi S.W. A perspective on structural and computational work on collagen. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016;18:24802–24811. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

