Changes of respiratory syncytial virus infection in children before and after the COVID-19 pandemic in Henan, China
- PMID: 36528226
- PMCID: PMC9751002
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2022.12.011
Changes of respiratory syncytial virus infection in children before and after the COVID-19 pandemic in Henan, China
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest None.
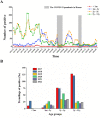
Figures

Comment on
-
Changes in Streptococcus pneumoniae infection in children before and after the COVID-19 pandemic in Zhengzhou, China.J Infect. 2022 Sep;85(3):e80-e81. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2022.05.040. Epub 2022 Jun 1. J Infect. 2022. PMID: 35659542 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Changes of Haemophilus influenzae infection in children before and after the COVID-19 pandemic, Henan, China.J Infect. 2023 Jan;86(1):66-117. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2022.10.019. Epub 2022 Oct 20. J Infect. 2023. PMID: 36273637 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bermudez Barrezueta L., Matias Del Pozo V., Lopez-Casillas P., Brezmes Raposo M., Gutierrez Zamorano M., Pino Vazquez M.A. Variation in the seasonality of the respiratory syncytial virus during the COVID-19 pandemic. Infection. 2022;50:1001–1005. doi: 10.1007/s15010-022-01794-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

