The effectiveness of intrauterine antibiotic infusion versus oral antibiotic therapy in the treatment of chronic endometritis in patients during IVF (in vitro fertilization) procedures
- PMID: 36528581
- PMCID: PMC9759887
- DOI: 10.1186/s12905-022-02128-8
The effectiveness of intrauterine antibiotic infusion versus oral antibiotic therapy in the treatment of chronic endometritis in patients during IVF (in vitro fertilization) procedures
Abstract
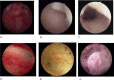
Background: Chronic Endometritis (CE) is a subtle pathology, likely infectious in most cases, with a negative impact on the female fertility, but often overlooked even among fertility specialists. The purpose of the study is to demonstrate the predominant infectious nature of CE and to find the best therapeutic option by comparing the results of oral antibiotic therapy versus intrauterine antibiotic infusion in patients with CE undergoing IVF procedures. The objective was to compare the cure rate of CE-defined as the percentage of patients without CE at the test of cure, between the two groups and, the hysteroscopic aspect with the positive CD 138 staining.
Methods: This was a prospective, case-control study that took place in a single university fertility clinic, in Oradea, Romania and included 57 patients with CE divided into 2 groups: orally administered antibiotics group who received a combination of antibiotics compared to intrauterine infusion group who received intrauterine infusion of antibiotic. Chronic Endometritis was diagnosed through hysteroscopy and immunohistochemistry for CD 138. Patients in both groups were tested for CE twice to evaluate the cure rate after oral combination antibiotic therapy versus intrauterine infusion of antibiotic.
Results: Out of 115 patients with endometrial biopsies 57 tested positive for CE, with a 49.6% chronic endometritis prevalence. Among the group that was administered oral antibiotics, 11 patients (45.83%) experienced CE resolution after triple antibiotic therapy. Of the intrauterine infusion group, 25 patients (89.29%) presented negative results (p 0.0020). The normal hysteroscopic aspect had a similar prevalence in the patients with immunohistochemical positive and negative CD 138.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrated the effectiveness and superiority of intrauterine antibiotic infusion over the use of oral combination antibiotic therapy for CE cure.
Trial registration: ISRCTN17542620/14.09.2022.
Keywords: Chronic endometritis; Hysteroscopy; Immunohistochemistry for CD 138; Intrauterine antibiotic infusion; Oral antibiotic therapy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.
Figures

References
-
- Moreno I, Cicinelli E, Garcia-Grau I, Gonzalez-Monfort M, Bau D, Vilella F, et al. The diagnosis of chronic endometritis in infertile asymptomatic women: a comparative study of histology, microbial cultures, hysteroscopy, and molecular microbiology. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;218:602e1–616. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2018.02.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cicinelli E, Haimovich S, De Ziegle RD, Raz N, Ben-Tzur D, Andrisani A, Ambrosini G, Picardi N, Cataldo V, Balzani M, Cicinelli R, Noventa M, Marin L, Greco P, Resta L, Saccardi C, Buzzaccarini G, Vitagliano A, International Working Group for Standardization of Chronic Endometritis Diagnosis MUM-1 immunohistochemistry has high accuracy and reliability in the diagnosis of chronic endometritis: a multi-centre comparative study with CD-138 immunostaining. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2021 doi: 10.1007/s10815-021-02356-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

