Roles of RNA-binding proteins in neurological disorders, COVID-19, and cancer
- PMID: 36528839
- PMCID: PMC9760055
- DOI: 10.1007/s13577-022-00843-w
Roles of RNA-binding proteins in neurological disorders, COVID-19, and cancer
Abstract
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) have emerged as important players in multiple biological processes including transcription regulation, splicing, R-loop homeostasis, DNA rearrangement, miRNA function, biogenesis, and ribosome biogenesis. A large number of RBPs had already been identified by different approaches in various organisms and exhibited regulatory functions on RNAs' fate. RBPs can either directly or indirectly interact with their target RNAs or mRNAs to assume a key biological function whose outcome may trigger disease or normal biological events. They also exert distinct functions related to their canonical and non-canonical forms. This review summarizes the current understanding of a wide range of RBPs' functions and highlights their emerging roles in the regulation of diverse pathways, different physiological processes, and their molecular links with diseases. Various types of diseases, encompassing colorectal carcinoma, non-small cell lung carcinoma, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, aberrantly express RBPs. We also highlight some recent advances in the field that could prompt the development of RBPs-based therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: Cancer; Neurodegenerative diseases; Post-transcriptional gene regulation; RNA; RNA processing; RNA-binding proteins; Viral infection.
© 2022. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Japan Human Cell Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
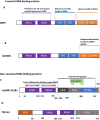
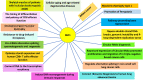

References
-
- Hoefig KP, Reim A, Gallus C, Wong EH, Behrens G, Conrad C, Xu M, Kifinger L, Ito-Kureha T, Defourny KAY, Geerlof A, Mautner J, Hauck SM, Baumjohann D, Feederle R, Mann M, Wierer M, Glasmacher E, Heissmeyer V. ‘Defining the RBPome of primary T helper cells to elucidate higher-order Roquin-mediated mRNA regulation. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):5208. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25345-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schneider T, Hung L-H, Aziz M, Wilmen A, Thaum S, Wagner J, Janowski R, Müller S, Schreiner S, Friedhoff P, Hüttelmaier S, Niessing D, Sattler M, Schlundt A, Bindereif A. Combinatorial recognition of clustered RNA elements by the multidomain RNA-binding protein IMP3. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):2266. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09769-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huang H, Weng H, Sun W, Qin X, Shi H, Wu H, Zhao BS, Mesquita A, Liu C, Yuan CL, Hu Y-C, Hüttelmaier S, Skibbe JR, Su R, Deng X, Dong L, Sun M, Li C, Nachtergaele S, Wang Y, Hu C, Ferchen K, Greis KD, Jiang X, Wei M, Qu L, Guan J-L, He C, Yang J, Chen J. Recognition of RNA N6-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA stability and translation. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20(3):285–295. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0045-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

