Antibiofilm Activity of PEGylated Branched Polyethylenimine
- PMID: 36530285
- PMCID: PMC9753512
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c04911
Antibiofilm Activity of PEGylated Branched Polyethylenimine
Abstract
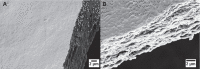
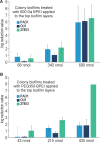
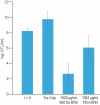
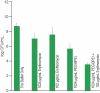
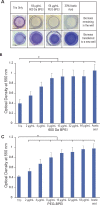
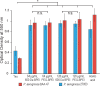
Biofilm formation is an adaptive resistance mechanism that pathogens employ to survive in the presence of antimicrobials. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an infectious Gram-negative bacterium whose biofilm allows it to withstand antimicrobial attack and threaten human health. Chronic wound healing is often impeded by P. aeruginosa infections and the associated biofilms. Previous findings demonstrate that 600 Da branched polyethylenimine (BPEI) can restore β-lactam potency against P. aeruginosa and disrupt its biofilms. Toxicity concerns of 600 Da BPEI are mitigated by covalent linkage with low-molecular-weight polyethylene glycol (PEG), and, in this study, PEGylated BPEI (PEG350-BPEI) was found exhibit superior antibiofilm activity against P. aeruginosa. The antibiofilm activity of both 600 Da BPEI and its PEG derivative was characterized with fluorescence studies and microscopy imaging. We also describe a variation of the colony biofilm model that was employed to evaluate the biofilm disruption activity of BPEI and PEG-BPEI.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bhargava A.; Hayakawa K.; Silverman E.; Haider S.; Alluri K. C.; Datla S.; Diviti S.; Kuchipudi V.; Muppavarapu K. S.; Lephart P. R.; Marchaim D.; Kaye K. S. Risk factors for colonization due to carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae among patients exposed to long-term acute care and acute care facilities. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2014, 35 (4), 398–405. 10.1086/675614. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Marchaim D.; Chopra T.; Bogan C.; Bheemreddy S.; Sengstock D.; Jagarlamudi R.; Malani A.; Lemanek L.; Moshos J.; Lephart P. R.; Ku K.; Hasan A.; Lee J.; Khandker N.; Blunden C.; Geffert S. F.; Moody M.; Hiro R.; Wang Y.; Ahmad F.; Mohammadi T.; Faruque O.; Patel D.; Pogue J. M.; Hayakawa K.; Dhar S.; Kaye K. S. The burden of multidrug-resistant organisms on tertiary hospitals posed by patients with recent stays in long-term acute care facilities. Am. J. Infect Control 2012, 40 (8), 760–5. 10.1016/j.ajic.2011.09.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Henig O.; Cober E.; Richter S. S.; Perez F.; Salata R. A.; Kalayjian R. C.; Watkins R. R.; Marshall S.; Rudin S. D.; Domitrovic T. N.; Hujer A. M.; Hujer K. M.; Doi Y.; Evans S.; Fowler V. G. Jr.; Bonomo R. A.; van Duin D.; Kaye K. S. Antibacterial Resistance Leadership, G. A Prospective Observational Study of the Epidemiology, Management, and Outcomes of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Due to Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Open Forum Infect Dis 2017, 4 (3), ofx157.10.1093/ofid/ofx157. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

