Trend of metabolic risk factors among the population aged 25-64 years for non-communicable diseases over time in Vietnam: A time series analysis using national STEPs survey data
- PMID: 36530703
- PMCID: PMC9747924
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1045202
Trend of metabolic risk factors among the population aged 25-64 years for non-communicable diseases over time in Vietnam: A time series analysis using national STEPs survey data
Abstract
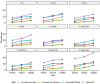
Introduction: The study aims to examine the trends of 4 metabolic NCDs risk factors including raised blood pressure, increased blood glucose, elevated blood lipids and overweight/obesity over the last 10 years in Vietnam as well as examine these trends among different sub-population by geographical area, gender, and age groups.
Methods: The study combined the national representative data from three rounds of STEPs survey in Vietnam conducted in 2010, 2015, and 2020 on people aged 25-64 years. The overall prevalence of each metabolic factor together with 95% CI for each time point as well as the stratified prevalence by rural/urban, male/female, and 4 separated age groups were calculated and considered the sampling weight. Cochran-Armitage test for trend was used to test for the differences in the prevalence over time.
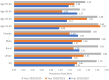
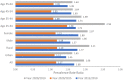
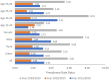
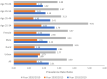
Results: The prevalence of hypertension, overweight/obesity, hyperglycemia, and hyperlipidemia among the population aged 25-64 years old was 28.3, 20.57, 6.96, and 15.63%, respectively in the year 2020. All NCD metabolic risk factors examined in this analysis show significantly increasing trends over time. For most age groups, the increasing burden of NCD metabolic risk factors was more significant during the period 2015-2020 compared to the period 2010-2015. Male population and population aged 55-64 experienced the most dramatic changes in the burden of all NCD metabolic risk factors.
Conclusion: To reverse the increasing trend of NCD metabolic factors in Vietnam, intervention, and policy need to apply a comprehensive life course approach.
Keywords: NCD; STEPs; metabolic risk factor; time series analyses; trend.
Copyright © 2022 Vu, Bui, Khuong, Tran, Lai and Hoang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Noncommunicable diseases country profiles 2018. World Health Organization (2018). p. 223. Available online at: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/274512 (accessed August 22, 2022).
-
- 2015 STEPS Country report Viet Nam. Available online at: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/2015-steps-country-report-viet-nam (accessed August 22, 2022).
-
- Government of Vietnam . Decision 155/QD-TTg about National Plan for prevention and control of NCDs and mental health diseases period 2022-2025.
-
- STEPS instrument for Noncommunicable Disease Surveillance Monitoring and Reporting. Available online at: https://www.who.int/teams/noncommunicable-diseases/surveillance/systems-... (accessed August 22, 2022).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

