Immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients undergoing autologous stem cell transplantation. A multicentric experience
- PMID: 36531008
- PMCID: PMC9755510
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.897937
Immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients undergoing autologous stem cell transplantation. A multicentric experience
Abstract
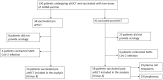
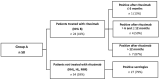
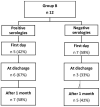
COVID-19 disease has a strong impact on hematological patients; those receiving autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (aHSCT) represent a particularly vulnerable group, in which the effectiveness of vaccination is very variable. Chiarucci et al. showed that patients affected by non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and treated with rituximab experienced a lower rate of immunization against SARS-CoV-2 (54%), as well as significantly lower IgG antibody titers. In our multicenter retrospective observational study, we included 82 patients who underwent aHSCT, divided into two groups: 58 patients vaccinated after aHSCT (group A) and 24 vaccinated before getting transplantation (group B). In group A, 39 (67%) patients had positive serology, and the rate of positivity increased with time after aHSCT. In the subgroup of patients with NHL, the administration of rituximab predicted negative serology, particularly when administered in the 6 months before vaccination (13% response rate). Patients affected by plasma cells had a higher rate of positivity (83% overall), independently of the time to aHSCT. In group B, no patient who initially showed positive serology became negative after transplantation, so the aHSCT did not affect the response to the vaccination. Our study confirmed the role of rituximab as a negative predictor of response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, whereas the conditioning and transplantation procedure itself seemed to be less important.
Keywords: SARSC-CoV-2; autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT); efficacy; rituximab; vaccination.
Copyright © 2022 Autore, Stirparo, Innocenti, Papa, Marchesi, Togni, Mariani, Torrieri, Salvatori, Fazio, Metafuni, Giammarco, Sora, Falcucci, Ferrari, Trisolini, Capria, Tafuri, Chiusolo, Sica and Laurenti.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sharma A, Bhatt NS, St Martin A, Abid MB, Bloomquist J, Chemaly RF, et al. . Clinical characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 in haematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients: an observational cohort study. Lancet Haematol (2021) 8(6):e393. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30429-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alpdogan O, Hong J, Klumpp TR, Abdulkareem A, Binder AF, Carabasi M, et al. . Vaccination response after autologous stem cell transplantation. Blood (2020) 136:25–6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2020-141269 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

