Inhibition of Prostaglandin E2 Receptor EP3 Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Apoptosis Partially by Modulating p38MAPK/FOXO3/Mul1/Mfn2 Pathway after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats
- PMID: 36531208
- PMCID: PMC9757947
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7727616
Inhibition of Prostaglandin E2 Receptor EP3 Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Apoptosis Partially by Modulating p38MAPK/FOXO3/Mul1/Mfn2 Pathway after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats
Abstract
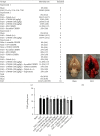
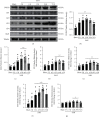
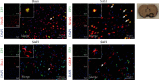
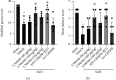
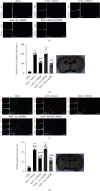
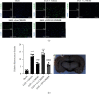
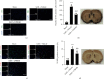
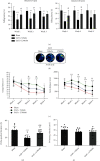
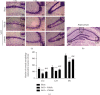
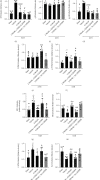
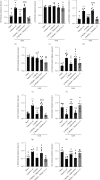
Oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis contribute to pathological processes of early brain injury (EBI) after subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). Previous studies demonstrated that the inhibition of prostaglandin E2 receptor EP3 suppressed oxidative stress and apoptotic effects after Alzheimer's disease and intracerebral hemorrhage. This study is aimed at investigating the antioxidative stress and antiapoptotic effect of EP3 inhibition and the underlying mechanisms in a rat mode of SAH. A total of 263 Sprague-Dawley male rats were used. SAH was induced by endovascular perforation. Selective EP3 antagonist L798106 was administered intranasally at 1 h, 25 h, and 49 h after SAH induction. EP3 knockout CRISPR and FOXO3 activation CRISPR were administered intracerebroventricularly at 48 h prior to SAH, while selective EP3 agonist sulprostone was administered at 1 h prior to SAH. SAH grade, neurological deficits, western blots, immunofluorescence staining, Fluoro-Jade C staining, TUNEL staining, 8-OHdG staining, and Nissl staining were conducted after SAH. The expression of endogenous PGES2 increased and peaked at 12 h while the expression of EP1, EP2, EP3, EP4, and Mul1 increased and peaked at 24 h in the ipsilateral brain after SAH. EP3 was expressed mainly in neurons. The inhibition of EP3 with L798106 or EP3 KO CRISPR ameliorated the neurological impairments, brain tissue oxidative stress, and neuronal apoptosis after SAH. To examine potential downstream mediators of EP3, we examined the effect of the increased expression of activated FOXO3 following the administration of FOXO3 activation CRISPR. Mechanism studies demonstrated that L798106 treatment significantly decreased the expression of EP3, p-p38, p-FOXO3, Mul1, 4-HNE, Bax, and cleaved caspase-3 but upregulated the expression of Mfn2 and Bcl-2 in SAH rats. EP3 agonist sulprostone or FOXO3 activation CRISPR abolished the neuroprotective effects of L798106 and its regulation on expression of p38MAPK/FOXO3/Mul1/Mfn2 in the ipsilateral brain after SAH. In conclusion, the inhibition of EP3 by L798106 attenuated oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis partly through p38MAPK/FOXO3/Mul1/Mfn2 pathway post-SAH in rats. EP3 may serve as a potential therapeutic target for SAH patients.
Copyright © 2022 Yu Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

