COVID-19 health data analysis and personal data preserving: A homomorphic privacy enforcement approach
- PMID: 36531214
- PMCID: PMC9747234
- DOI: 10.1016/j.comcom.2022.12.004
COVID-19 health data analysis and personal data preserving: A homomorphic privacy enforcement approach
Abstract
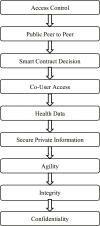
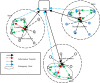
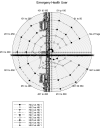
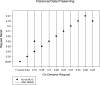
COVID-19 data analysis and prediction from patient data repository collected from hospitals and health organizations. Users' credentials and personal information are at risk; it could be an unrecoverable issue worldwide. A Homomorphic identification of possible breaches could be more appropriate for minimizing the risk factors in preventing personal data. Individual user privacy preservation is a must-needed research focus in various fields. Health data generated and collected information from multiple scenarios increasing the complexity involved in maintaining secret patient information. A homomorphic-based systematic approach with a deep learning process could reduce depicts and illegal functionality of unknown organizations trying to have relation to the environment and physical and social relations. This article addresses the homomorphic standard system functionality, which refers to all the functional aspects of deep learning system requirements in COVID-19 health management. Moreover, this paper spotlights the metric privacy incorporation for improving the Deep Learning System (DPLS) approaches for solving the healthcare system's complex issues. It is absorbed from the result analysis Homomorphic-based privacy observation metric gradually improves the effectiveness of the deep learning process in COVID-19-health care management.
Keywords: Deep learning system; Healthcare; Homomorphic; Privacy metrics; Privacy preserving; Security.
© 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Is Homomorphic Encryption-Based Deep Learning Secure Enough?Sensors (Basel). 2021 Nov 24;21(23):7806. doi: 10.3390/s21237806. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34883809 Free PMC article.
-
Homomorphic Encryption-Based Federated Privacy Preservation for Deep Active Learning.Entropy (Basel). 2022 Oct 27;24(11):1545. doi: 10.3390/e24111545. Entropy (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36359635 Free PMC article.
-
Towards realistic privacy-preserving deep learning over encrypted medical data.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Apr 28;10:1117360. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1117360. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37187785 Free PMC article.
-
Privacy-preserving deep learning for pervasive health monitoring: a study of environment requirements and existing solutions adequacy.Health Technol (Berl). 2022;12(2):285-304. doi: 10.1007/s12553-022-00640-3. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Health Technol (Berl). 2022. PMID: 35136708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precision health data: Requirements, challenges and existing techniques for data security and privacy.Comput Biol Med. 2021 Feb;129:104130. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.104130. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33271399 Review.
Cited by
-
Achieving sustainable medical tourism: unpacking privacy concerns through a tripartite game theoretic lens.Front Public Health. 2024 Apr 9;12:1347231. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1347231. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38655509 Free PMC article.
-
An anonymization-based privacy-preserving data collection protocol for digital health data.Front Public Health. 2023 Mar 3;11:1125011. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1125011. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36935661 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in Clinical and Laboratory Features of Pregnant and Non-Pregnant Female with Hospitalized COVID-19.Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2025 May 8;30(3):322-331. doi: 10.4103/ijnmr.ijnmr_86_23. eCollection 2025 May-Jun. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2025. PMID: 40520400 Free PMC article.
-
Computer-aided analysis of radiological images for cancer diagnosis: performance analysis on benchmark datasets, challenges, and directions.EJNMMI Rep. 2024 Apr 1;8(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s41824-024-00195-8. EJNMMI Rep. 2024. PMID: 38748374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adversarial Attack and Defense in Breast Cancer Deep Learning Systems.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Aug 17;10(8):973. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10080973. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fedele G., Russo G., Schiavoni I., Leone P., Olivetta E., Perri V., Zingaropoli M.A., Ciardi M.R., Pasculli P., Mastroianni C.M., Stefanelli P. Early IgG/ IgA response in hospitalized COVID-19 patients is associated with a less severe disease. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2022;102(1) doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2021.115586. Epub 2021 Oct 23. PMID: 34742119; PMCID: PMC8539217. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
