Prognostic implications of necroptosis-related long noncoding RNA signatures in muscle-invasive bladder cancer
- PMID: 36531246
- PMCID: PMC9755502
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1036098
Prognostic implications of necroptosis-related long noncoding RNA signatures in muscle-invasive bladder cancer
Abstract
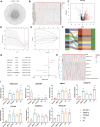
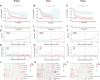
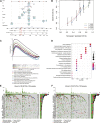
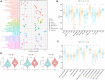
Background: Bladder cancer (BLCA) is the sixth most common cancer in men, with an increasing incidence of morbidity and mortality. Necroptosis is a type of programmed cell death and plays a critical role in the biological processes of bladder cancer (BLCA). However, current studies focusing on long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) and necroptosis in cancer are limited, and there is no research about necroptosis-related lncRNAs (NRLs) in BLCA. Methods: We obtained the RNA-seq data and corresponding clinical information of BLCA from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. The seven determined prognostic NLRs were analyzed by several methods and verified by RT-qPCR. Then, a risk signature was established based on the aforementioned prognostic NLRs. To identify it, we evaluated its prognostic value by Kaplan-Meier (K-M) survival curve and receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve analysis. Moreover, the relationships between risk signature and clinical features, functional enrichment, immune landscape, and drug resistance were explored as well. Results: We constructed a signature based on seven defined NLRs (HMGA2-AS1, LINC02489, ETV7-AS1, EMSLR, AC005954.1, STAG3L5P-PVRIG2P-PILRB, and LINC02178). Patients in the low-risk cohort had longer survival times than those in the high-risk cohort, and the area under the ROC curve (AUC) value of risk signature was higher than other clinical variables. Functional analyses, the infiltrating level of immune cells and functions, ESTIMATE score, and immune checkpoint analysis all indicated that the high-risk group was in a relatively immune-activated state. In terms of treatments, patients in the high-risk group were more sensitive to immunotherapy, especially anti-PD1/PD-L1 immunotherapy and conventional chemotherapy. Conclusion: The novel NLR signature acts as an invaluable tool for predicting prognosis, immune microenvironment, and drug resistance in muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) patients.
Keywords: drug resistance; immune microenvironment; lncRNAs; muscle-invasive bladder cancer; necroptosis; prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 Jiang, Wu, Yin, Tang, Yin, Zhou, Yu and Yan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of a novel defined inflammation-related long noncoding RNA signature contributes to predicting prognosis and distinction between the cold and hot tumors in bladder cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 29;13:972558. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.972558. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37064115 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Characterization of Necroptosis-Related lncRNAs in Bladder Cancer Identifies a Novel Signature for Prognosis Prediction.Dis Markers. 2022 Jun 6;2022:2360299. doi: 10.1155/2022/2360299. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35711565 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Prognosis and Distinguishing Cold and Hot Tumors in Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Based on Necroptosis-Associated lncRNAs.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 4;13:916800. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.916800. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35860239 Free PMC article.
-
A five necroptosis-related lncRNA signature predicts the prognosis of bladder cancer and identifies hot or cold tumors.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Oct 13;102(41):e35196. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035196. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37832111 Free PMC article.
-
A novel necroptosis-related lncRNA signature for predicting prognosis and anti-cancer treatment response in endometrial cancer.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 16;13:1018544. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1018544. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36466815 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
HPV-Associated Gene Signatures in Bladder Cancer: A Comprehensive Prognostic Model and its Implications in Immunotherapy.Int J Med Sci. 2025 Jan 1;22(1):140-157. doi: 10.7150/ijms.98334. eCollection 2025. Int J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39744172 Free PMC article.
-
The fate and function of non-coding RNAs during necroptosis.Epigenomics. 2024;16(11-12):901-915. doi: 10.1080/17501911.2024.2354653. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Epigenomics. 2024. PMID: 38884366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of a Novel Disulfidptosis-Related lncRNA Prognostic Signature in Pancreatic Cancer.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Sep;66(9):2396-2414. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00875-z. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37733182
-
Construction of lncRNA prognostic model related to disulfidptosis in lung adenocarcinoma.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 3;10(15):e35657. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35657. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170273 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the prognosis, immune response, and immunotherapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma using a novel risk model based on anoikis-related lncRNAs.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Nov 28;28(1):548. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01521-9. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 38017579 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahlen Bergman E., Hartana C. A., Johansson M., Linton L. B., Berglund S., Hyllienmark M., et al. (2018). Increased CD4(+) T cell lineage commitment determined by CpG methylation correlates with better prognosis in urinary bladder cancer patients. Clin. Epigenetics 10 (1), 102. 10.1186/s13148-018-0536-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

