Evaluation of an Artificial Intelligence System for Retinopathy of Prematurity Screening in Nepal and Mongolia
- PMID: 36531583
- PMCID: PMC9754980
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xops.2022.100165
Evaluation of an Artificial Intelligence System for Retinopathy of Prematurity Screening in Nepal and Mongolia
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the performance of a deep learning (DL) algorithm for retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) screening in Nepal and Mongolia.
Design: Retrospective analysis of prospectively collected clinical data.
Participants: Clinical information and fundus images were obtained from infants in 2 ROP screening programs in Nepal and Mongolia.
Methods: Fundus images were obtained using the Forus 3nethra neo (Forus Health) in Nepal and the RetCam Portable (Natus Medical, Inc.) in Mongolia. The overall severity of ROP was determined from the medical record using the International Classification of ROP (ICROP). The presence of plus disease was determined independently in each image using a reference standard diagnosis. The Imaging and Informatics for ROP (i-ROP) DL algorithm was trained on images from the RetCam to classify plus disease and to assign a vascular severity score (VSS) from 1 through 9.
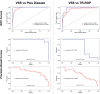
Main outcome measures: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve and area under the precision-recall curve for the presence of plus disease or type 1 ROP and association between VSS and ICROP disease category.
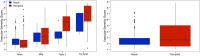
Results: The prevalence of type 1 ROP was found to be higher in Mongolia (14.0%) than in Nepal (2.2%; P < 0.001) in these data sets. In Mongolia (RetCam images), the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for examination-level plus disease detection was 0.968, and the area under the precision-recall curve was 0.823. In Nepal (Forus images), these values were 0.999 and 0.993, respectively. The ROP VSS was associated with ICROP classification in both datasets (P < 0.001). At the population level, the median VSS was found to be higher in Mongolia (2.7; interquartile range [IQR], 1.3-5.4]) as compared with Nepal (1.9; IQR, 1.2-3.4; P < 0.001).
Conclusions: These data provide preliminary evidence of the effectiveness of the i-ROP DL algorithm for ROP screening in neonatal populations in Nepal and Mongolia using multiple camera systems and are useful for consideration in future clinical implementation of artificial intelligence-based ROP screening in low- and middle-income countries.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; BW, birth weight; DL, deep learning; Deep learning; GA, gestational age; ICROP, International Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity; IQR, interquartile range; LMIC, low- and middle-income country; Mongolia; Nepal; ROP, retinopathy of prematurity; RSD, reference standard diagnosis; Retinopathy of prematurity; TR, treatment-requiring; VSS, vascular severity score; i-ROP, Imaging and Informatics for Retinopathy of Prematurity.
© 2022 by the American Academy of Ophthalmology.
Figures
References
-
- Gilbert C. Retinopathy of prematurity: a global perspective of the epidemics, population of babies at risk and implications for control. Early Hum Dev. 2008;84(2):77–82. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert C., Fielder A., Gordillo L., et al. Characteristics of infants with severe retinopathy of prematurity in countries with low, moderate, and high levels of development: implications for screening programs. Pediatrics. 2005;115(5):e518–e525. - PubMed
-
- Dogra M.R., Katoch D. Clinical features and characteristics of retinopathy of prematurity in developing countries. Ann Eye Sci. 2018;3(1):1–7.
-
- Shah P.K., Ramya A., Narendran V. Telemedicine for ROP. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila) 2018;7(1):52–55. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

