Krebs von den lungen-6 as a clinical marker for hypersensitivity pneumonitis: A meta-analysis and bioinformatics analysis
- PMID: 36532009
- PMCID: PMC9748086
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1041098
Krebs von den lungen-6 as a clinical marker for hypersensitivity pneumonitis: A meta-analysis and bioinformatics analysis
Abstract
Aim: Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP), also referred to as exogenous allergic alveolitis, is one of the most common interstitial lung diseases (ILDs). A potential immune biomarker, Krebs von den lgen-6 (KL-6) characterizes the progression and severity of HP. The meta-analysis in this study was conducted to elucidate the variations in the concentrations of KL-6 in different types of HP.
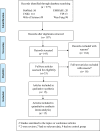
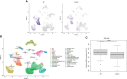
Methods: A systematic search of various databases such as EMBASE, Pubmed, CNKI, VIP, Web of Science, and WanFang was carried out to find relevant published articles between January 1980 and August 2022 that explored the relationship between KL-6 and allergic pneumonia. Standardized mean difference (SMD) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were used as effect sizes for comparison among different groups. The GSE47460 and GSE150910 datasets were downloaded to extract and validate the differences in KL-6 mRNA expression between HP lung tissue and healthy controls. Furthermore, the single-cell sequencing dataset GSE135893 was downloaded to extract KL-6 mRNA expression in type II alveolar epithelial cells to validate the differences between HP and healthy controls. Two researchers evaluated the quality of the included studies by employing Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. All the qualified studies were subjected to statistical analyses carried out utilizing RevMan 5.2, Stata 11.0, and R software 4.1.3.
Results: Twenty studies aligned perfectly with the inclusion criteria of the meta. The concentrations of KL-6 were substantially higher in the blood of HP patients as compared to the control group. Subgroup analyses were carried out in accordance with the allergen source and the results revealed that patients with different allergens had higher blood KL-6 concentrations than healthy controls. Additionally, different subgroups of subjects were created for meta-analysis as per the fibrosis status, race, measurement method, and sample type. The concentration of KL-6 in blood was much higher in all HP subgroups than in healthy control groups. Moreover, the bioinformatics analysis revealed that KL-6 mRNA expression was higher in HP lung tissue and type II alveolar epithelial cells as compared to healthy controls.
Conclusion: The present meta-analysis and bioinformatics analysis suggested that the concentration levels of KL-6 varied between HP patients and healthy individuals, and the KL-6 concentrations may be higher in the blood samples of HP patients.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, CRD42022355334.
Keywords: Krebs von den Lungen-6; bioinformatics analysis; hypersensitivity pneumonitis; meta-analysis; systematic review.
Copyright © 2022 He, Zhang and Ren.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



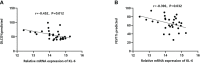

Similar articles
-
YKL-40 and KL-6 Levels in Serum and Sputum of Patients Diagnosed With Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2022 Sep;10(9):2414-2423. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2022.06.031. Epub 2022 Jul 2. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2022. PMID: 35788062
-
The usefulness of KL-6 and SP-D for the diagnosis and management of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis.Respir Med. 2015 Dec;109(12):1576-81. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2015.10.005. Epub 2015 Oct 16. Respir Med. 2015. PMID: 26481343
-
Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6) is a pathophysiological biomarker of early-stage acute hypersensitivity pneumonitis among pigeon fanciers.Clin Exp Allergy. 2020 Dec;50(12):1391-1399. doi: 10.1111/cea.13744. Epub 2020 Oct 4. Clin Exp Allergy. 2020. PMID: 32966647
-
Biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 29;15:1455346. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1455346. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39534599 Free PMC article.
-
Krebs von den Lungen-6 as a biomarker for disease severity assessment in interstitial lung disease: a comprehensive review.Biomark Med. 2020 Jun;14(8):665-674. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2019-0545. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Biomark Med. 2020. PMID: 32613855 Review.
Cited by
-
Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6) as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for non-neoplastic lung diseases.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2024 Nov 27;63(5):923-930. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2024-1089. Print 2025 Apr 28. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2024. PMID: 39589105
-
Serum KL-6 and the mortality of patients with connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: A meta-analysis.Biomol Biomed. 2024 Sep 6;24(5):1105-1116. doi: 10.17305/bb.2024.10368. Biomol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38743787 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Exacerbations of Interstitial Lung Diseases: Focus on Biomarkers.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 15;24(12):10196. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210196. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effectiveness and pharmacoeconomic study of using different corticosteroids in the treatment of hypersensitivity pneumonitis.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Feb 15;24(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-02896-z. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 38360614 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Progression in Pulmonary Fibrosis: An Overview of Underlying Mechanisms, Molecular Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Intervention.Life (Basel). 2024 Feb 6;14(2):229. doi: 10.3390/life14020229. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38398739 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

