Distinctive phenotype for HLA-E- versus HLA-A2-restricted memory CD8 αβT cells in the course of HCMV infection discloses features shared with NKG2C+CD57+NK and δ2-γδT cell subsets
- PMID: 36532017
- PMCID: PMC9752567
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1063690
Distinctive phenotype for HLA-E- versus HLA-A2-restricted memory CD8 αβT cells in the course of HCMV infection discloses features shared with NKG2C+CD57+NK and δ2-γδT cell subsets
Abstract
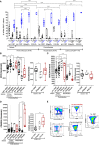
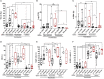
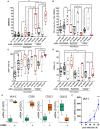
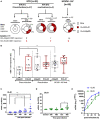
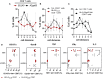
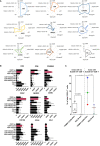
The human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) triggers both innate and adaptive immune responses, including protective CD8+ αβT cells (CD8T) that contributes to the control of the infection. In addition to CD8T restricted by classical HLA class Ia molecules, HCMV also triggers CD8T recognizing peptides from the HCMV UL40 leader peptide and restricted by HLA-E molecules (HLA-EUL40 CD8T). This study investigated the frequency, phenotype and functions of HLA-EUL40 CD8T in comparison to the immunodominant HLA-A2pp65 CD8T upon acute (primary or secondary infection) or chronic infection in kidney transplant recipients (KTR) and in seropositive (HCMV+) healthy volunteer (HV) hosts. The frequency of hosts with detected HLA-EUL40 CD8T was similar after a primary infection (24%) and during viral latency in HCMV+ HV (26%) and equal to the frequency of HLA-A2pp65 CD8T cells in both conditions (29%). Both CD8T subsets vary from 0.1% to >30% of total circulating CD8T according to the host. Both HLA-EUL40 and HLA-A2pp65 CD8T display a phenotype specific of CD8+ TEMRA (CD45RA+/CCR7-) but HLA-EUL40 CD8T express distinctive level for CD3, CD8 and CD45RA. Tim3, Lag-3, 4-1BB, and to a lesser extend 2B4 are hallmarks for T cell priming post-primary infection while KLRG1 and Tigit are markers for restimulated and long lived HCMV-specific CD8T responses. These cell markers are equally expressed on HLA-EUL40 and HLA-A2pp65 CD8T. In contrast, CD56 and PD-1 are cell markers discriminating memory HLA-E- from HLA-A2-restricted CD8T. Long lived HLA-EUL40 display higher proliferation rate compared to HLA-A2pp65 CD8T consistent with elevated CD57 expression. Finally, a comparative immunoprofiling indicated that HLA-EUL40 CD8T, divergent from HLA-A2pp65 CD8T, share the expression of CD56, CD57, NKG2C, CD158 and the lack of PD-1 with NKG2C+CD57+ NK and δ2-γδT cells induced in response to HCMV and thus defines a common immunopattern for these subsets.
Keywords: CD56; CD8 T cells; HCMV; HLA-E; NK; PD-1; γδT.
Copyright © 2022 Rousselière, Gérard, Delbos, Guérif, Giral, Bressollette-Bodin and Charreau.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Changes in HCMV immune cell frequency and phenotype are associated with chronic lung allograft dysfunction.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 28;14:1143875. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1143875. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37187736 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping and Characterization of HCMV-Specific Unconventional HLA-E-Restricted CD8 T Cell Populations and Associated NK and T Cell Responses Using HLA/Peptide Tetramers and Spectral Flow Cytometry.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 27;23(1):263. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010263. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008688 Free PMC article.
-
HCMV triggers frequent and persistent UL40-specific unconventional HLA-E-restricted CD8 T-cell responses with potential autologous and allogeneic peptide recognition.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Apr 30;14(4):e1007041. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007041. eCollection 2018 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29709038 Free PMC article.
-
Features of Memory-Like and PD-1(+) Human NK Cell Subsets.Front Immunol. 2016 Sep 14;7:351. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00351. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27683578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular characterization of HCMV-specific immune responses: Parallels between CD8(+) T cells, CD4(+) T cells, and NK cells.Eur J Immunol. 2015 Sep;45(9):2433-45. doi: 10.1002/eji.201545495. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26228786 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural killer cell memory: challenges and opportunities for cancer immunotherapy.Cancer Biol Ther. 2024 Dec 31;25(1):2376410. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2024.2376410. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Cancer Biol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38987282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification a unique disulfidptosis classification regarding prognosis and immune landscapes in thyroid carcinoma and providing therapeutic strategies.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Oct;149(13):11157-11170. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05006-4. Epub 2023 Jun 22. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37347261 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in HCMV immune cell frequency and phenotype are associated with chronic lung allograft dysfunction.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 28;14:1143875. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1143875. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37187736 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent CD8 T Cell Marks Caused by the HCMV Infection in Seropositive Adults: Prevalence of HLA-E-Reactive CD8 T Cells.Cells. 2023 Mar 14;12(6):889. doi: 10.3390/cells12060889. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36980230 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

