Resident macrophages of the lung and liver: The guardians of our tissues
- PMID: 36532044
- PMCID: PMC9750759
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1029085
Resident macrophages of the lung and liver: The guardians of our tissues
Abstract
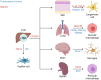
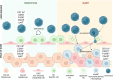
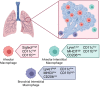
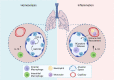
Resident macrophages play a unique role in the maintenance of tissue function. As phagocytes, they are an essential first line defenders against pathogens and much of the initial characterization of these cells was focused on their interaction with viral and bacterial pathogens. However, these cells are increasingly recognized as contributing to more than just host defense. Through cytokine production, receptor engagement and gap junction communication resident macrophages tune tissue inflammatory tone, influence adaptive immune cell phenotype and regulate tissue structure and function. This review highlights resident macrophages in the liver and lung as they hold unique roles in the maintenance of the interface between the circulatory system and the external environment. As such, we detail the developmental origin of these cells, their contribution to host defense and the array of tools these cells use to regulate tissue homeostasis.
Keywords: Kupffer cells; alveolar macrophages; homeostasis; inflammation; interstitial macrophages; liver; lung; macrophages.
Copyright © 2022 Kulle, Thanabalasuriar, Cohen and Szydlowska.
Conflict of interest statement
TSC and MS are employed by AstraZeneca. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting hepatic macrophages to treat liver diseases.J Hepatol. 2017 Jun;66(6):1300-1312. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.02.026. Epub 2017 Mar 4. J Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28267621 Review.
-
Tissues use resident dendritic cells and macrophages to maintain homeostasis and to regain homeostasis upon tissue injury: the immunoregulatory role of changing tissue environments.Mediators Inflamm. 2012;2012:951390. doi: 10.1155/2012/951390. Epub 2012 Dec 3. Mediators Inflamm. 2012. PMID: 23251037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
M-CSF Mediates Host Defense during Bacterial Pneumonia by Promoting the Survival of Lung and Liver Mononuclear Phagocytes.J Immunol. 2016 Jun 15;196(12):5047-55. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600306. Epub 2016 May 4. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27183631 Free PMC article.
-
The guardians of pulmonary harmony: alveolar macrophages orchestrating the symphony of lung inflammation and tissue homeostasis.Eur Respir Rev. 2024 May 29;33(172):230263. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0263-2023. Print 2024 Apr 30. Eur Respir Rev. 2024. PMID: 38811033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophages and polymorphonuclear neutrophils in lung defense and injury.Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Feb;141(2):471-501. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.2.471. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990. PMID: 2405761 Review.
Cited by
-
Macrophages and stem/progenitor cells interplay in adipose tissue and skeletal muscle: a review.Stem Cell Investig. 2023 Apr 13;10:9. doi: 10.21037/sci-2023-009. eCollection 2023. Stem Cell Investig. 2023. PMID: 37077316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myeloid cells in chronic liver inflammation.Cell Mol Immunol. 2025 Jul 28. doi: 10.1038/s41423-025-01324-4. Online ahead of print. Cell Mol Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40721870 Review.
-
Liver immunology: Biological role and clinical significance.World J Hepatol. 2025 Jul 27;17(7):107541. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i7.107541. World J Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40747238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quercetin Alleviates Pulmonary Fibrosis in Silicotic Mice by Inhibiting Macrophage Transition and TGF-β-Smad2/3 Pathway.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Apr 5;45(4):3087-3101. doi: 10.3390/cimb45040202. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37185726 Free PMC article.
-
Opposite effects of systemic and local conditional CD11c+ myeloid cell depletion during bleomycin-induced inflammation and fibrosis in mice.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Nov;12(11):e70042. doi: 10.1002/iid3.70042. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 39582275 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

