Novel organic selenium source hydroxy-selenomethionine counteracts the blood-milk barrier disruption and inflammatory response of mice under heat stress
- PMID: 36532046
- PMCID: PMC9757697
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1054128
Novel organic selenium source hydroxy-selenomethionine counteracts the blood-milk barrier disruption and inflammatory response of mice under heat stress
Abstract
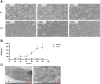
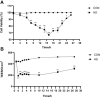
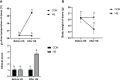
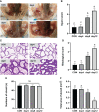
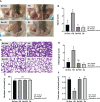
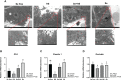
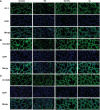
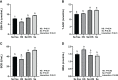
Heat stress (HS) in summer has caused huge economic losses to animal husbandry production recently. When mammary gland is exposed to high temperatures, it will cause blood-milk barrier damage. Hydroxy-selenomethionine (HMSeBA) is a new selenium source with better guarantee of animals' production performance under stress, but whether it has protective effect on heat stress-induced blood-milk damage is still unclear. We established mammary epithelial cells and mice heat stress injury models to fill this research gap, and hope to provide theoretical basis for using HMSeBA to alleviate heat stress damage mammary gland. The results showed that (1) Heat stress significantly decreases in vitro transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) and cell viability (P < 0.01), and significantly decreases clinical score, histological score, and total alveoli area of mice mammary gland tissue (P < 0.01). (2) HMSeBA significantly increases TEER and fluorescein sodium leakage of HS-induced monolayer BMECs (P < 0.01), significantly improves the milk production and total area of alveoli (P < 0.01), and reduces clinical score, histological score, mRNA expression of heat stress-related proteins, and inflammatory cytokines release of heat-stressed mice (P < 0.01). (3) HMSeBA significantly improves tight junction structure damage, and significantly up-regulated the expression of tight junction proteins (ZO-1, claudin 1, and occludin) as well as signal molecules PI3K, AKT, and mTOR (P < 0.01) in heat-stressed mammary tissue. (4) HMSeBA significantly increases glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), and superoxide dismutase release (SOD) (P < 0.01) and significantly reduce malondialdehyde (MDA) expression (P < 0.01) in heat-stressed mammary tissue. In conclusion, this study implemented heat-stressed cell and mice model and showed that HMSeBA significantly regulate antioxidant capacity, inhibited inflammation, and regulate tight junction proteins expression in blood-milk barrier via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, so as to alleviate mammary gland damage and ensure its structure and function integrity.
Keywords: antioxidant activity; blood-milk barrier; heat stress; hydroxy-selenomethionine; inflammatory response.
Copyright © 2022 Zheng, Zhao, He, Wang, Cao, Yang, Wang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
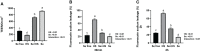
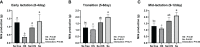
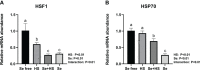
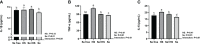
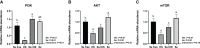
Similar articles
-
Hydroxy-selenomethionine helps cows to overcome heat stress by enhancing antioxidant capacity and alleviating blood-milk barrier damage.Anim Nutr. 2024 Nov 7;20:171-181. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2024.10.003. eCollection 2025 Mar. Anim Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39967694 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of source on bioavailability of selenium, antioxidant status, and performance in lactating dairy cows during oxidative stress-inducing conditions.J Dairy Sci. 2019 Jan;102(1):311-319. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-14974. Epub 2018 Oct 19. J Dairy Sci. 2019. PMID: 30343914
-
Hydroxy-selenomethionine: A novel organic selenium source that improves antioxidant status and selenium concentrations in milk and plasma of mid-lactation dairy cows.J Dairy Sci. 2017 Dec;100(12):9602-9610. doi: 10.3168/jds.2017-12610. Epub 2017 Oct 4. J Dairy Sci. 2017. PMID: 28987589
-
Symposium review: The influences of heat stress on bovine mammary gland function.J Dairy Sci. 2018 Jun;101(6):5642-5654. doi: 10.3168/jds.2017-13727. Epub 2018 Jan 10. J Dairy Sci. 2018. PMID: 29331468 Review.
-
Effects of Selenium as a Dietary Source on Performance, Inflammation, Cell Damage, and Reproduction of Livestock Induced by Heat Stress: A Review.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 18;12:820853. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.820853. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35116042 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Butyrolactone-I from Marine Fungal Metabolites Mitigates Heat-Stress-Induced Apoptosis in IPEC-J2 Cells and Mice Through the ROS/PERK/CHOP Signaling Pathway.Mar Drugs. 2024 Dec 17;22(12):564. doi: 10.3390/md22120564. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39728139 Free PMC article.
-
Tanshinone IIA protects mouse testes from heat stress injury by inhibiting apoptosis and TGFβ1/Smad2/Smad3 signaling pathway.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023 Nov;28(6):749-759. doi: 10.1007/s12192-023-01367-4. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023. PMID: 37610501 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxy-selenomethionine helps cows to overcome heat stress by enhancing antioxidant capacity and alleviating blood-milk barrier damage.Anim Nutr. 2024 Nov 7;20:171-181. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2024.10.003. eCollection 2025 Mar. Anim Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39967694 Free PMC article.
-
Selenium Counteracts Tight Junction Disruption and Attenuates the NF-κB-Mediated Inflammatory Response in Staphylococcus aureus-Infected Mouse Mammary Glands.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Feb;203(2):963-972. doi: 10.1007/s12011-024-04210-8. Epub 2024 Apr 27. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 38676878
-
Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Selenium-Deficient MAC-T Cells Aggravated Inflammation and Apoptosis by Triggering the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Stress/PI3K-AKT-mTOR Pathway in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Dec 5;12(12):2077. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122077. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lindsay SJ. Hand-held pneumatic impact tool and method of controlling the same. U.S. Patent No 6095256. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. (2000).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

