Bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study of causality between rheumatoid arthritis and myocardial infarction
- PMID: 36532051
- PMCID: PMC9755576
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1017444
Bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study of causality between rheumatoid arthritis and myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: Epidemiological evidence suggests an association between rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and myocardial infarction (MI). However, causality remains uncertain. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the causal association between RA and MI.
Methods: Using publicly available genome-wide association study summary datasets, bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization (TSMR) was performed using inverse-variance weighted (IVW), weighted median, MR-Egger regression, simple mode, and weighted mode methods.
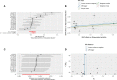
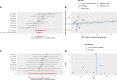
Results: The MR results for the causal effect of RA on MI (IVW, odds ratio [OR] = 1.041, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.007-1.076, P = 0.017; weighted median, OR = 1.027, 95% CI: 1.006-1.049, P = 0.012) supported a causal association between genetic susceptibility to RA and an increased risk of MI. MR results for the causal effect of MI on RA (IVW, OR = 1.012, 95% CI: 0.807-1.268, P = 0.921; weighted median, OR = 1.069, 95% CI: 0.855-1.338, P = 0.556) indicated that there was no causal association between genetic susceptibility to MI and an increased risk of RA.
Conclusion: Bidirectional TSMR analysis supports a causal association between genetic susceptibility to RA and an increased risk of MI but does not support a causal association between genetic susceptibility to MI and an increased risk of RA.
Keywords: bidirectional; causal association; myocardial infarction; rheumatoid arthritis; two-sample Mendelian randomization study.
Copyright © 2022 Guo, Wang, Peng and Yuan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rheumatoid arthritis is a protective factor against Alzheimer's disease: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Feb;32(1):863-871. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01397-5. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38151584
-
Causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and bronchiectasis: a bidirectional mendelian randomization study.Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 May 23;26(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03336-3. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38783321 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Sleep Traits and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Mendelian Randomization Study.Front Public Health. 2022 Jun 30;10:940161. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.940161. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35844889 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the causal relationship between immune cells and rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of genetic variation: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Adv Rheumatol. 2024 Nov 1;64(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s42358-024-00425-4. Adv Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39487558 Review.
-
Association of telomere length with risk of rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis and Mendelian randomization.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020 May 1;59(5):940-947. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez524. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020. PMID: 31697380
Cited by
-
Rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of fracture: A Mendelian randomization study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jan 17;104(3):e41248. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041248. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 39833078 Free PMC article.
-
A Guide to Understanding Mendelian Randomization Studies.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2024 Nov;76(11):1451-1460. doi: 10.1002/acr.25400. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 39030941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Causal Relationship Between Childhood Obesity and Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Bidirectional Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Analysis.Nat Sci Sleep. 2024 Oct 22;16:1713-1723. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S477435. eCollection 2024. Nat Sci Sleep. 2024. PMID: 39464513 Free PMC article.
-
GWAS advancements to investigate disease associations and biological mechanisms.Clin Transl Discov. 2024 Jul;4(3):e296. doi: 10.1002/ctd2.296. Epub 2024 May 1. Clin Transl Discov. 2024. PMID: 38737752 Free PMC article.
-
Bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study of association between smoking initiation and atrial fibrillation.Tob Induc Dis. 2024 Jun 19;22. doi: 10.18332/tid/189380. eCollection 2024. Tob Induc Dis. 2024. PMID: 38899119 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical