Resolvin D2 induces anti-microbial mechanisms in a model of infectious peritonitis and secondary lung infection
- PMID: 36532055
- PMCID: PMC9754689
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1011944
Resolvin D2 induces anti-microbial mechanisms in a model of infectious peritonitis and secondary lung infection
Abstract
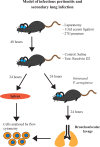
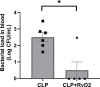
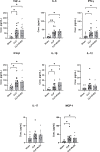
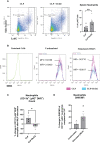
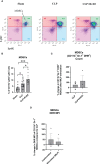
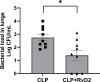
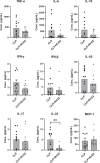
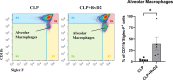
In severe bacterial infections, there is a pro-inflammatory response to promote bacterial clearance but this response can cause tissue injury. Later, the immune system becomes dysregulated and the host is unable to clear a secondary or a pre-existing infection. Specialized Pro-resolving Mediators (SPMs) such as resolvin D2 (RvD2) have been shown to be beneficial for inflammation/infection resolution in animal models of sepsis but in vivo mechanisms by which RvD2 may promote bacterial clearance and/or attenuate deleterious effects of a secondary infection have not been fully established. In this study, we used the 2-hit model of cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) induced infectious peritonitis and secondary lung infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa to find possible antimicrobial and immunomodulatory mechanisms of RvD2. We show that RvD2 given as late as 48h after CLP surgery reduced blood bacterial load without altering plasma cytokines compared to mice given saline vehicle. RvD2 increased splenic neutrophil accumulation as well as average reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. There was also an increase in an immature leukocyte population the myeloid derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) in the spleen of RvD2 treated mice. RvD2 reduced lung lavage bacterial load 24h after P. aeruginosa administration and significantly decreased lung lavage levels of IL-23, a cytokine essential in the Th-17 inflammatory response. In addition, we show that RvD2 increased the number of non-inflammatory alveolar macrophages after P. aeruginosa administration compared to saline treated mice. The study uncovered an antimicrobial mechanism of RvD2 where RvD2 increases mature neutrophil and MDSC accumulation into the spleen to promote blood bacterial clearance. The study showed that in this 2-hit model, RvD2 promotes lung bacterial clearance, increased non-inflammatory alveolar macrophage number and inhibits an adaptive immune pathway providing evidence of its resolution mechanism in secondary pulmonary infection.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; alveolar macrophages; cytokines; inflammation; innate immunity; myeloid-derived suppressor cells; neutrophils; specialized pro-resolving mediators.
Copyright © 2022 Sundarasivarao, Walker, Rodriguez, Spur and Yin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Uncovering the Power of GPR18 Signalling: How RvD2 and Other Ligands Could Have the Potential to Modulate and Resolve Inflammation in Various Health Disorders.Molecules. 2024 Mar 12;29(6):1258. doi: 10.3390/molecules29061258. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38542895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low-dose pro-resolving mediators temporally reset the resolution response to microbial inflammation.Mol Med. 2024 Sep 18;30(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00877-w. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39294573 Free PMC article.
-
Resolvin D2 promotes host defense in a 2 - hit model of sepsis with secondary lung infection.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2022 Apr;159:106617. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2022.106617. Epub 2022 Jan 8. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2022. PMID: 35007703 Free PMC article.
-
Resolvin D2 attenuates LPS-induced macrophage exhaustion.FASEB J. 2024 Apr 15;38(7):e23569. doi: 10.1096/fj.202302521R. FASEB J. 2024. PMID: 38551610
-
Immunosuppression in Sepsis: Biomarkers and Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators.Biomedicines. 2024 Jan 13;12(1):175. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010175. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38255280 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Uncovering the Power of GPR18 Signalling: How RvD2 and Other Ligands Could Have the Potential to Modulate and Resolve Inflammation in Various Health Disorders.Molecules. 2024 Mar 12;29(6):1258. doi: 10.3390/molecules29061258. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38542895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is Lipid Metabolism of Value in Cancer Research and Treatment? Part II: Role of Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators in Inflammation, Infections, and Cancer.Metabolites. 2024 May 29;14(6):314. doi: 10.3390/metabo14060314. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38921449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid mediators in neutrophil biology: inflammation, resolution and beyond.Curr Opin Hematol. 2024 Jul 1;31(4):175-192. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000822. Epub 2024 May 7. Curr Opin Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38727155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential of exogenous specialized pro-resolving mediators in protecting against sepsis-associated lung injury: a review.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 29;16:1622754. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1622754. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40799817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low-dose pro-resolving mediators temporally reset the resolution response to microbial inflammation.Mol Med. 2024 Sep 18;30(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00877-w. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39294573 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

