Kinetics of free and ligand-bound atacicept in human serum
- PMID: 36532058
- PMCID: PMC9756848
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1035556
Kinetics of free and ligand-bound atacicept in human serum
Abstract
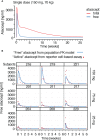
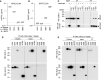
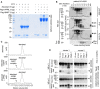
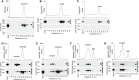
BAFF (B cell activation factor of the TNF family/B lymphocyte stimulator, BLyS) and APRIL (a proliferation-inducing ligand) are targeted by atacicept, a decoy receptor consisting of the extracellular domain of TACI (transmembrane activator and calcium-modulator and cyclophilin (CAML) interactor) fused to the Fc portion of human IgG1. The purpose of the study was to characterize free and ligand-bound atacicept in humans. Total and active atacicept in serum of healthy volunteers receiving a single dose of subcutaneous atacicept or in patients treated weekly for one year were measured by ELISA, Western blot, or cell-based assays. Pharmacokinetics of free and bound atacicept were predicted based on total atacicept ELISA results. Persistence of complexes of purified atacicept bound to recombinant ligands was also monitored in mice. Results show that unbound or active atacicept in human serum exceeded 0.1 µg/ml for one week post administration, or throughout a 1-year treatment with weekly administrations. After a single administration of atacicept, endogenous BAFF bound to atacicept was detected after 8 h then increased about 100-fold within 2 to 4 weeks. Endogenous heteromers of BAFF and APRIL bound to atacicept also accumulated, but atacicept-APRIL complexes were not detected. In mice receiving intravenous injections of purified complexes pre-formed in vitro, atacicept-BAFF persisted longer (more than a week) than atacicept-APRIL (less than a day). Thus, only biologically inactive BAFF and BAFF-APRIL heteromers accumulate on atacicept in vivo. The measure of active atacicept provides further support for the once-weekly dosing regimen implemented in the clinical development of atacicept.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00624338.
Keywords: APRIL; BAFF; atacicept; heteromers; reporter cells.
Copyright © 2022 Eslami, Willen, Papasouliotis, Schuepbach-Mallpell, Willen, Donzé, Yalkinoglu and Schneider.
Conflict of interest statement
PS was supported by a research grant from Merck Healthcare KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany. OP is employee of Merck Institute for Pharmacometrics, Lausanne, Switzerland, an affiliate of Merck KGaA. ÖY and DW were employee of Merck Healthcare KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany at the time of the study. OD was employed by Adipogen Life Sciences. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
No interactions between heparin and atacicept, an antagonist of B cell survival cytokines.Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Oct;176(20):4019-4033. doi: 10.1111/bph.14811. Epub 2019 Oct 15. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31355456 Free PMC article.
-
B-lymphocyte stimulator/a proliferation-inducing ligand heterotrimers are elevated in the sera of patients with autoimmune disease and are neutralized by atacicept and B-cell maturation antigen-immunoglobulin.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(2):R48. doi: 10.1186/ar2959. Epub 2010 Mar 19. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20302641 Free PMC article.
-
Atacicept (TACI-Ig) inhibits growth of TACI(high) primary myeloma cells in SCID-hu mice and in coculture with osteoclasts.Leukemia. 2008 Feb;22(2):406-13. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2405048. Epub 2007 Nov 29. Leukemia. 2008. PMID: 18046446 Free PMC article.
-
The role of BAFF and APRIL in rheumatoid arthritis.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug;234(10):17050-17063. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28445. Epub 2019 Apr 2. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30941763 Review.
-
Systematic Review of Safety and Efficacy of Atacicept in Treating Immune-Mediated Disorders.Front Immunol. 2020 Mar 24;11:433. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00433. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32265917 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A first-in-human, randomized study of the safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of povetacicept, an enhanced dual BAFF/APRIL antagonist, in healthy adults.Clin Transl Sci. 2024 Nov;17(11):e70055. doi: 10.1111/cts.70055. Clin Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39494621 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Population pharmacokinetics of atacicept in systemic lupus erythematosus: An analysis of three clinical trials.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2023 Aug;12(8):1157-1169. doi: 10.1002/psp4.12982. Epub 2023 Jun 18. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37332136 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Dall'Era M, Chakravarty E, Wallace D, Genovese M, Weisman M, Kavanaugh A, et al. . Reduced b lymphocyte and immunoglobulin levels after atacicept treatment in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Results of a multicenter, phase ib, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalating trial. Arthritis Rheumatol (2007) 56(12):4142–50. doi: 10.1002/art.23047 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dillon SR, Harder B, Lewis KB, Moore MD, Liu H, Bukowski TR, et al. . B-lymphocyte stimulator/a proliferation-inducing ligand heterotrimers are elevated in the sera of patients with autoimmune disease and are neutralized by atacicept and b-cell maturation antigen-immunoglobulin. Arthritis Res Ther (2010) 12(2):R48. doi: 10.1186/ar2959 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

