FCGR2C: An emerging immune gene for predicting sepsis outcome
- PMID: 36532072
- PMCID: PMC9757160
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1028785
FCGR2C: An emerging immune gene for predicting sepsis outcome
Abstract
Background: Sepsis is a life-threatening disease associated with immunosuppression. Immunosuppression could ultimately increase sepsis mortality. This study aimed to identify the prognostic biomarkers related to immunity in sepsis.
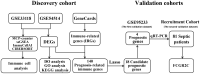
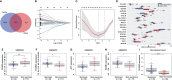
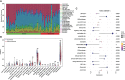
Methods: Public datasets of sepsis downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database were divided into the discovery cohort and the first validation cohort. We used R software to screen differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and analyzed DEGs' functional enrichment in the discovery dataset. Immune-related genes (IRGs) were filtered from the GeneCards website. A Lasso regression model was used to screen candidate prognostic genes from the intersection of DEGs and IRGs. Then, the candidate prognostic genes with significant differences were identified as prognostic genes in the first validation cohort. We further validated the expression of the prognostic genes in the second validation cohort of 81 septic patients recruited from our hospital. In addition, we used four immune infiltration methods (MCP-counter, ssGSEA, ImmuCellAI, and CIBERSORT) to analyze immune cell composition in sepsis. We also explored the correlation between the prognostic biomarker and immune cells.
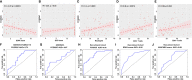
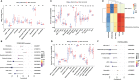
Results: First, 140 genes were identified as prognostic-related immune genes from the intersection of DEGs and IRGs. We screened 18 candidate prognostic genes in the discovery cohort with the lasso regression model. Second, in the first validation cohort, we identified 4 genes (CFHR2, FCGR2C, GFI1, and TICAM1) as prognostic immune genes. Subsequently, we found that FCGR2C was the only gene differentially expressed between survivors and non-survivors in 81 septic patients. In the discovery and first validation cohorts, the AUC values of FCGR2C were 0.73 and 0.67, respectively. FCGR2C (AUC=0.84) had more value than SOFA (AUC=0.80) and APACHE II (AUC=0.69) in evaluating the prognosis of septic patients in our recruitment cohort. Moreover, FCGR2C may be closely related to many immune cells and functions, such as B cells, NK cells, neutrophils, cytolytic activity, and inflammatory promotion. Finally, enrichment analysis showed that FCGR2C was enriched in the phagosome signaling pathway.
Conclusion: FCGR2C could be an immune biomarker associated with prognosis, which may be a new direction of immunotherapy to reduce sepsis mortality.
Keywords: FCGR2C; immune genes; prognosis; prognostic biomarker; sepsis.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Zhang, Zhang, Zhao and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

