How does China's stock market react to supply chain disruptions from COVID-19?
- PMID: 36532085
- PMCID: PMC9040410
- DOI: 10.1016/j.irfa.2022.102168
How does China's stock market react to supply chain disruptions from COVID-19?
Abstract
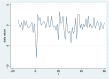
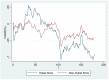
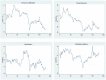
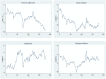
As a once-in-a-century global pandemic, COVID-19 severely hit the global economy and disrupted the worldwide supply chain. Based on 505 Chinese firms, we use the event study method to explore the effect of COVID-19 on the financial performance of firms. The findings show that COVID-19 has an immediate impact on Chinese firms. Hubei firms experience stronger effects than non-Hubei firms. Supply chain disruptions effects from COVID-19 are observed. Transportation industry is hit more severely than retail industry. Insurance companies experience a strong adverse effect. On the other hand, both medical and competitor firms experience significantly positive spillover effects.
Keywords: Abnormal returns; COVID-19; Event study; Supply chain disruption.
© 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative evidence on the impact of the COVID-19 outbreak and vaccine discovery on the global transportation industry.Transp Res Interdiscip Perspect. 2023 Jan;17:100741. doi: 10.1016/j.trip.2022.100741. Epub 2023 Jan 2. Transp Res Interdiscip Perspect. 2023. PMID: 36618962 Free PMC article.
-
Financial performance of China's listed firms in presence of coronavirus: Evidence from corporate culture and corporate social responsibility.Curr Psychol. 2023;42(11):8897-8918. doi: 10.1007/s12144-021-02200-w. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Curr Psychol. 2023. PMID: 34400856 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Consumer Behavior-Evidence From China's Stock Market.Front Public Health. 2022 Sep 6;10:865470. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.865470. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36148367 Free PMC article.
-
The time-varying spillover effect of China's stock market during the COVID-19 pandemic.Physica A. 2022 Oct 1;603:127821. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2022.127821. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Physica A. 2022. PMID: 35782685 Free PMC article.
-
Supply chain resilience: Measure, risk assessment and strategies.Fundam Res. 2023 Apr 19;5(2):433-436. doi: 10.1016/j.fmre.2023.03.011. eCollection 2025 Mar. Fundam Res. 2023. PMID: 40242524 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative evidence on the impact of the COVID-19 outbreak and vaccine discovery on the global transportation industry.Transp Res Interdiscip Perspect. 2023 Jan;17:100741. doi: 10.1016/j.trip.2022.100741. Epub 2023 Jan 2. Transp Res Interdiscip Perspect. 2023. PMID: 36618962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adda J. Economic activity and the spread of viral diseases: Evidence from high frequency data. Quarterly Journal of Economics. 2016;131(2):891–941.
-
- Aktas N., de Bodt E., Derbaix A. Horizontal, downstream and upstream effects of merger & acquisition operations in the car industry. 2003. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/237335316 Available at.
-
- AlAli M.S. The effect of WHO COVID-19 announcement on Asian stock markets returns: An event study analysis. Journal of Economics and Business. 2020;3(3):1051–1054.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
