Multi Epitopic Peptide Based Vaccine Development Targeting Immobilization Antigen of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis: A Computational Approach
- PMID: 36532362
- PMCID: PMC9734321
- DOI: 10.1007/s10989-022-10475-1
Multi Epitopic Peptide Based Vaccine Development Targeting Immobilization Antigen of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis: A Computational Approach
Abstract
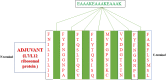
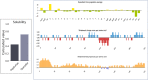
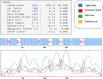
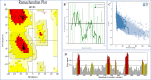
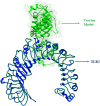
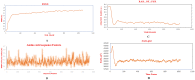
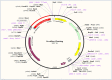
The white spot disease causes significant damage to global aquaculture production. A prominent vaccine, eliciting the immunogenicity of freshwater fishes against Ichthyophthirius multifiliis yet to be developed. Thus, an Immunoinformatic drive was implemented to find out the potential epitopes from the surface immobilization antigens. B-cell derived T-cell epitopes are promiscuous elements for new generation peptide-based vaccine designing. A total of eight common B and T-cell epitopes had filtered out with no overlapping manner. Subsequently, the common epitopes are linked up with EAAAKEAAAKEAAAK linker peptides, we also added L7/L12 ribosomal protein adjuvant at the N- terminal side of peptide sequence for eliciting the immune response in a better way. The secondary and tertiary structural properties of the modeled 3D protein revealed that the protein had all the properties required for a protective immunogen. Afterward, three globally used validation server: PROCKECK, ProSA and ERRAT were used to justify the proper coordinate. NMR, Crystallographic range and error plot calculation for vaccine model also been done respectively. This was followed by molecular docking, MD simulation, NMA analysis, in silico cloning and vaccine dose-based immune response simulation to evaluate the immunogenic potency of the vaccine construct. The in silico immune simulation in response to multi-epitopes show antibody generation and elevated levels of cell-mediated immunity during repeated exposure of the vaccine. The favourable results of the in silico analysis significantly specify that the vaccine construct is really a powerful vaccine candidate and ready to proceed to the next steps of experimental validation and efficacy studies.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s10989-022-10475-1.
Keywords: B-cell; Docking; Immunoinformatics; MD simulation; NMA; Spot disease; T-cell.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V. 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
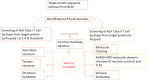
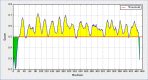
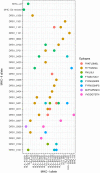
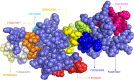



Similar articles
-
A Novel Multi-Epitopic Peptide Vaccine Candidate Against Helicobacter pylori: In-Silico Identification, Design, Cloning and Validation Through Molecular Dynamics.Int J Pept Res Ther. 2021;27(2):1149-1166. doi: 10.1007/s10989-020-10157-w. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Int J Pept Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33495694 Free PMC article.
-
Designing a next generation multi-epitope based peptide vaccine candidate against SARS-CoV-2 using computational approaches.3 Biotech. 2021 Feb;11(2):47. doi: 10.1007/s13205-020-02574-x. Epub 2021 Jan 11. 3 Biotech. 2021. PMID: 33457172 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoinformatics assisted profiling of West Nile virus proteome to determine immunodominant epitopes for the development of next-generation multi-peptide vaccine.Front Immunol. 2024 May 10;15:1395870. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1395870. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38799422 Free PMC article.
-
An integrated multi-pronged reverse vaccinology and biophysical approaches for identification of potential vaccine candidates against Nipah virus.Saudi Pharm J. 2023 Dec;31(12):101826. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.101826. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Saudi Pharm J. 2023. PMID: 38028215 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a multi-epitope peptide vaccine inducing robust T cell responses against brucellosis using immunoinformatics based approaches.Infect Genet Evol. 2017 Jul;51:227-234. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2017.04.009. Epub 2017 Apr 11. Infect Genet Evol. 2017. PMID: 28411163
Cited by
-
Riding the wave of innovation: immunoinformatics in fish disease control.PeerJ. 2023 Dec 8;11:e16419. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16419. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 38089909 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- ABDULLAH-AL MAMUN M, et al. Mass infection of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis in two ornamental fish and their control measures. Ann Biol. 2021;37(2):209–214.
-
- Andrews C. The ornamental fish trade and fish conservation. J Fish Biol. 1990;37:53–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8649.1990.tb05020.x. - DOI
-
- Basu A, Dutta D, Banerjee S. Indigenous ornamental fishes of west Bengal. Recent Res Sci Technol. 2012;4(11):12–21.
-
- Biotech, G.J.U.s.c., SnapGene software [web]. 2015
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
