(2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine acts through GluA1-induced synaptic plasticity to alleviate PTSD-like effects in rat models
- PMID: 36532380
- PMCID: PMC9755068
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2022.100503
(2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine acts through GluA1-induced synaptic plasticity to alleviate PTSD-like effects in rat models
Abstract
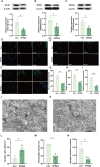
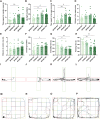
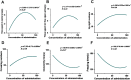
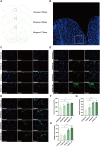
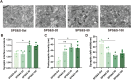
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a debilitating mental disorder with high morbidity and great social and economic relevance. However, extant pharmacotherapies of PTSD require long-term use to maintain effectiveness and have enormous side effects. The glutamatergic system, especially the α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPAR), is an important target of current research on the mechanism of PTSD. Postsynaptic AMPAR function and expression are known to be increased by (2R, 6R)-hydronorketamine (HNK), the primary metabolite of ketamine. However, whether (2R,6R)-HNK alleviates PTSD-like effects via AMPAR upregulation is yet to be known. In the present study, rats were exposed to single prolonged stress and electric foot shock (SPS&S). Afterwards, gradient concentrations of (2R,6R)-HNK (20, 50, and 100 μM) were administered by intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) injection. Open field, elevated plus maze, freezing behavior, and forced swimming tests were used to examine PTSD-like symptoms. In addition, the protein levels of GluA1, BDNF and PSD-95 were analyzed using western blotting and immunofluorescence, and the synaptic ultrastructure of the prefrontal cortex (PFC) was observed by transmission electron microscopy. We found that (2R,6R)-HNK changed SPS&S-induced behavioral expression, such as increasing autonomous activity and residence time in the open arm and decreasing immobility time. Likewise, (2R,6R)-HNK (50 μM) increased GluA1, BDNF, and PSD-95 protein expression in the PFC. Changes in synaptic ultrastructure induced by SPS&S were reversed by administration of (2R,6R)-HNK. Overall, we find that (2R,6R)-HNK can ameliorate SPS&S-induced fear avoidance in rats, as well as rat cognates of anxiety and depression. This may be related to GluA1-mediated synaptic plasticity in the PFC.
Keywords: (2R,6R)-Hydroxynorketamine ((2R,6R)-HNK); GluA1; Glutamatergic nervous system; Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD); Synaptic plasticity.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
(2R, 6R)-hydroxynorketamine ameliorates PTSD-like behaviors during the reconsolidation phase of fear memory in rats by modulating the VGF/BDNF/GluA1 signaling pathway in the hippocampus.Behav Brain Res. 2025 Jan 5;476:115273. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2024.115273. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Behav Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 39326635
-
(2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine improves PTSD-associated behaviors and structural plasticity via modulating BDNF-mTOR signaling in the nucleus accumbens.J Affect Disord. 2023 Aug 15;335:129-140. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.04.101. Epub 2023 May 1. J Affect Disord. 2023. PMID: 37137411
-
(2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine alleviates PTSD-like endophenotypes by regulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in rats.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2024 Dec;245:173891. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2024.173891. Epub 2024 Oct 5. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2024. PMID: 39369910
-
The antidepressant potential of (2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine: A detailed review of pre-clinical findings.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 15;999:177604. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177604. Epub 2025 Apr 8. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40209847 Review.
-
Hydroxynorketamines: Pharmacology and Potential Therapeutic Applications.Pharmacol Rev. 2021 Apr;73(2):763-791. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.120.000149. Pharmacol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33674359 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular pathways of ketamine: A systematic review of immediate and sustained effects on PTSD.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025 Jun;242(6):1197-1243. doi: 10.1007/s00213-025-06756-4. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025. PMID: 40097854 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of (2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine on oxycodone withdrawal and reinstatement.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2023 Dec 1;253:110987. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2023.110987. Epub 2023 Oct 5. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2023. PMID: 37864957 Free PMC article.
-
Social hierarchy and resilience affect stress-induced PTSD via Uba7 gene expression and subsequent inflammation in microglia of the mPFC.Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Aug 23. doi: 10.1038/s41380-025-03171-1. Online ahead of print. Mol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40849546
-
New Insights into Contradictory Changes in Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) in Rodent Models of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD).Neurochem Res. 2024 Dec;49(12):3226-3243. doi: 10.1007/s11064-024-04242-5. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 39283581 Review.
-
Anxiolytic effects of Enterococcus faecalis 2001 on a mouse model of colitis.Sci Rep. 2024 May 21;14(1):11519. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62309-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38769131 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blaze J., Navickas A., Phillips H.L., Heissel S., Plaza-Jennings A., Miglani S.…Akbarian S. Neuronal Nsun2 deficiency produces tRNA epitranscriptomic alterations and proteomic shifts impacting synaptic signaling and behavior. Nat. Commun. 2021;12(1):4913. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24969-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carliss R.D., R A., Chengelis C.P., O'Neill T.P., Shuey D.L. Oral administration of dextromethorphan does not produce neuronal vacuolation in the rat brain. Neurotoxicology. 2007;28(4):813–818. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

