A metabotropic glutamate receptor affects the growth and development of Schistosoma japonicum
- PMID: 36532433
- PMCID: PMC9750798
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1045490
A metabotropic glutamate receptor affects the growth and development of Schistosoma japonicum
Abstract
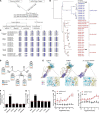
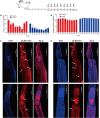
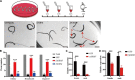
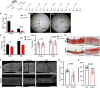
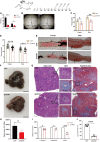
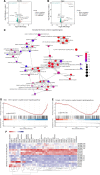
Schistosomiasis is a zoonotic parasitic disease caused by schistosome infection that severely threatens human health. Therapy relies mainly on single drug treatment with praziquantel. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop alternative medicines. The glutamate neurotransmitter in helminths is involved in many physiological functions by interacting with various cell-surface receptors. However, the roles and detailed regulatory mechanisms of the metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR) in the growth and development of Schistosoma japonicum remain poorly understood. In this study, we identified two putative mGluRs in S. japonicum and named them SjGRM7 (Sjc_001309, similar to GRM7) and SjGRM (Sjc_001163, similar to mGluR). Further validation using a calcium mobilization assay showed that SjGRM7 and SjGRM are glutamate-specific. The results of in situ hybridization showed that SjGRM is mainly located in the nerves of both males and gonads of females, and SjGRM7 is principally found in the nerves and gonads of males and females. In a RNA interference experiment, the results showed that SjGRM7 knockdown by double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) in S. japonicum caused edema, chassis detachment, and separation of paired worms in vitro. Furthermore, dsRNA interference of SjGRM7 could significantly affect the development and egg production of male and female worms in vivo and alleviate the host liver granulomas and fibrosis. Finally, we examined the molecular mechanisms underlying the regulatory function of mGluR using RNA sequencing. The data suggest that SjGRM7 propagates its signals through the G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway to promote nervous system development in S. japonicum. In conclusion, SjGRM7 is a potential target for anti-schistosomiasis. This study enables future research on the mechanisms of action of Schistosomiasis japonica drugs.
Keywords: Schistosoma japonicum; development; double-stranded RNA; liver fibrosis; metabotropic glutamate receptor.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Cheng, Chen, Zhang, Xie, Liu, You, Yi, Zhu, Gu, Xu, Lu, Wang and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Andrews S. (2013). FastQC: A quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. Available online at: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed November 20, 2020).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

