Natural products against inflammation and atherosclerosis: Targeting on gut microbiota
- PMID: 36532443
- PMCID: PMC9751351
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.997056
Natural products against inflammation and atherosclerosis: Targeting on gut microbiota
Abstract
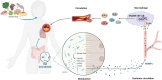
The gut microbiota (GM) has become recognized as a crucial element in preserving human fitness and influencing disease consequences. Commensal and pathogenic gut microorganisms are correlated with pathological progress in atherosclerosis (AS). GM may thus be a promising therapeutic target for AS. Natural products with cardioprotective qualities might improve the inflammation of AS by modulating the GM ecosystem, opening new avenues for researches and therapies. However, it is unclear what components of natural products are useful and what the actual mechanisms are. In this review, we have summarized the natural products relieving inflammation of AS by regulating the GM balance and active metabolites produced by GM.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; gut microbiota; immune; inflammation; natural products.
Copyright © 2022 Deng, Tao and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abdel-Latif M. A., Elbestawy A. R., El-Far A. H., Noreldin A. E., Emam M., Baty R. S., et al. . (2021). Quercetin dietary supplementation advances growth performance, gut microbiota, and intestinal mRNA expression genes in broiler chickens. Animals (Basel). 11:2302. doi: 10.3390/ani11082302, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aguilar E. C., Santos L. C., Leonel A. J., de Oliveira J. S., Santos E. A., Navia-Pelaez J. M., et al. . (2016). Oral butyrate reduces oxidative stress in atherosclerotic lesion sites by a mechanism involving NADPH oxidase down-regulation in endothelial cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 34, 99–105. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.05.002, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Asada M., Oishi E., Sakata S., Hata J., Yoshida D., Honda T., et al. . (2019). Serum lipopolysaccharide-binding protein levels and the incidence of cardiovascular disease in a general Japanese population: the Hisayama study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 8:e013628. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.013628, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

