Prolonged activity of HERV-K(HML2) in Old World Monkeys accounts for recent integrations and novel recombinant variants
- PMID: 36532485
- PMCID: PMC9751479
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1040792
Prolonged activity of HERV-K(HML2) in Old World Monkeys accounts for recent integrations and novel recombinant variants
Abstract
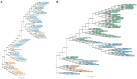
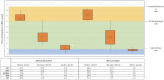
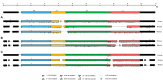
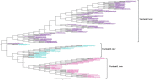
Around 8% of the human genome comprises Human Endogenous Retroviruses (HERVs) acquired over primate evolution. Some are specific to primates such as HERV-K, consisting of 10 HML subtypes and including the most recently acquired elements. Particularly, HML2 is the youngest clade, having some human-specific integrations, and while it has been widely described in humans its presence and distribution in non-human primates remain poorly characterized. To investigate HML2 distribution in non-human primates, the present study focused on the characterization of HML2 integrations in Macaca fascicularis and Macaca mulatta which are the most evolutionarily distant species related to humans in the Catarrhini parvorder. We identified overall 208 HML2 proviruses for M. fascicularis (77) and M. mulatta (131). Among them, 46 proviruses are shared by the two species while the others are species specific. Only 12 proviruses were shared with humans, confirming that the major wave of HML2 diffusion in humans occurred after macaques' divergence. Phylogenetic analysis confirmed structural variations between HML2 macaques' species-specific proviruses, and the ones shared between macaques and humans. The HML2 loci were characterized in terms of structure, focusing on potential residual open reading frames (ORFs) for gag, pol, and env genes for the latter being reported to be expressed in human pathological conditions. The analysis identified highly conserved gag and pol genes, while the env genes had a very divergent nature. Of the 208 HML2 proviral sequences present in Macaca species, 81 sequences form a cluster having a MER11A, a characteristic HML8 LTR sequence, insertion in the env region indicating a recombination event that occurred between the HML2 env gene and the HML8 LTR. This recombination event, which was shown to be present only in a subset of macaques' shared sequences and species-specific sequences, highlights a recent viral activity leading to the emergence of an env variant specific to the Old World Monkeys (OWMs). We performed an exhaustive analysis of HML2 in two species of OWMs, in terms of its evolutionary history, structural features, and potential residual coding capacity highlighting recent activity of HML2 in macaques that occurred after its split from the Catarrhini parvorder, leading to the emergence of viral variants, hence providing a better understanding of the endogenization and diffusion of HML2 along primate evolution.
Keywords: HERV-K; HERV-K11; HML2; Macaca; Old World Monkeys; endogenous retroviruses; recombination; viral evolution.
Copyright © 2022 Chabukswar, Grandi and Tramontano.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Recombinant origin and interspecies transmission of a HERV-K(HML-2)-related primate retrovirus with a novel RNA transport element.Elife. 2024 Jul 22;13:e80216. doi: 10.7554/eLife.80216. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39037763 Free PMC article.
-
Identification, comprehensive characterization, and comparative genomics of the HERV-K(HML8) integrations in the human genome.Virus Res. 2023 Jan 2;323:198976. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2022.198976. Epub 2022 Oct 26. Virus Res. 2023. PMID: 36309315 Free PMC article.
-
The HERV-K human endogenous retrovirus envelope protein antagonizes Tetherin antiviral activity.J Virol. 2014 Dec;88(23):13626-37. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02234-14. Epub 2014 Sep 10. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25210194 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular biology of type A endogenous retrovirus.Kitasato Arch Exp Med. 1990 Sep;63(2-3):77-90. Kitasato Arch Exp Med. 1990. PMID: 1710682 Review.
-
HERV-K: the biologically most active human endogenous retrovirus family.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1996;13 Suppl 1:S261-7. doi: 10.1097/00042560-199600001-00039. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1996. PMID: 8797733 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutation Rate Variation and Other Challenges in 2-LTR Dating of Primate Endogenous Retrovirus Integrations.J Mol Evol. 2025 Feb;93(1):62-82. doi: 10.1007/s00239-024-10225-5. Epub 2024 Dec 23. J Mol Evol. 2025. PMID: 39715846 Review.
-
Compilation of all known HERV-K HML-2 proviral integrations.Mob DNA. 2025 May 7;16(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s13100-025-00359-8. Mob DNA. 2025. PMID: 40336055 Free PMC article.
-
Envelope Recombination: A Major Driver in Shaping Retroviral Diversification and Evolution within the Host Genome.Viruses. 2023 Aug 31;15(9):1856. doi: 10.3390/v15091856. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37766262 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Belshaw R., Dawson A. L. A., Woolven-Allen J., Redding J., Burt A., Tristem M. (2005). Genomewide screening reveals high levels of Insertional polymorphism in the human endogenous retrovirus family HERV-K(HML2): implications for present-day activity. J. Virol. 79, 12507–12514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.79.19.12507-12514.2005, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

