A Chinese herbs complex ameliorates gut microbiota dysbiosis induced by intermittent cold exposure in female rats
- PMID: 36532488
- PMCID: PMC9748289
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1065780
A Chinese herbs complex ameliorates gut microbiota dysbiosis induced by intermittent cold exposure in female rats
Abstract
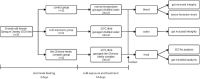
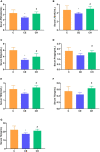
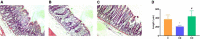
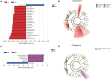
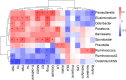
Cold is a common source of stress in the alpine areas of northern China. It affects the microbial community, resulting in the invasion of pathogenic microorganisms and intestinal diseases. In recent years, studies have reported that Chinese herbal extracts and their fermentation broth have a significant beneficial effect on gut microbiota. This study aimed to investigate the probiotic effect of a self-designed Chinese herbs complex on the gut microbiota of rats exposed to cold. The rats were treated with intermittent cold exposure and Chinese herbs complex for 14 days, and the gut microbiota composition and other parameters were assayed. The 16s ribosomal DNA high-throughput sequencing and analysis confirmed that the Chinese herbs complex positively improved the gut microbiota. We found that cold exposure could lead to significant changes in the composition of gut microbiota, and affect the intestinal barrier and other physiological functions. The relative abundance of some probiotics in the genus such as Roseburia, Parasutterella, and Elusimicrobium in rats treated with Chinese herbs complex was significantly increased. Serum D-lactic acid (D-LA) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were increased in the cold exposure group and decreased in the Chinese herbs complex-treated group. Moreover, the Chinese herbs complex significantly increased the protein expression of occludin. In conclusion, the Chinese herbs complex is effective in restoring the gut microbiota caused by cold exposure, improving the function of the intestinal barrier, and may act as a prebiotic in combatting gut dysbiosis.
Keywords: Chinese herbs complex; HPO axis; cold exposure; gut microbiota; intestinal barrier function.
Copyright © 2022 Jin, Bian, Dong, Yang, Jing, Li, Yang, Guo and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Gut dysbiosis induced by antibiotics is improved by tangerine pith extract in mice.Nutr Res. 2022 May;101:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2022.01.005. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Nutr Res. 2022. PMID: 35301159
-
Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota Is Associated With the Progression of Radiation-Induced Intestinal Injury and Is Alleviated by Oral Compound Probiotics in Mouse Model.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Oct 25;11:717636. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.717636. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34760714 Free PMC article.
-
Could the gut microbiota reconcile the oral bioavailability conundrum of traditional herbs?J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Feb 17;179:253-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.12.031. Epub 2015 Dec 23. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26723469 Review.
-
Divergent impacts on the gut microbiome and host metabolism induced by traditional Chinese Medicine with Cold or Hot properties in mice.Chin Med. 2022 Dec 26;17(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s13020-022-00697-2. Chin Med. 2022. PMID: 36572936 Free PMC article.
-
Prebiotic effects: metabolic and health benefits.Br J Nutr. 2010 Aug;104 Suppl 2:S1-63. doi: 10.1017/S0007114510003363. Br J Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20920376 Review.
Cited by
-
Gut microbiota contribute to cold adaptation in mammals-primates and ungulates.iScience. 2025 Mar 19;28(4):112245. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112245. eCollection 2025 Apr 18. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40241768 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory Effects of a Standardized Botanical Mixture Comprising Angelica gigas Roots and Pueraria lobata Flowers Through the TLR2/6 Pathway in RAW 264.7 Macrophages and Cyclophosphamide-Induced Immunosuppression Mice.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Feb 27;18(3):336. doi: 10.3390/ph18030336. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40143115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen K. (2020). Effects of fermented Danggui Buxue decoction on growth performance and intestinal microflora diversity in broilers. Master’s thesis. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

