Aeromonas species isolated from aquatic organisms, insects, chicken, and humans in India show similar antimicrobial resistance profiles
- PMID: 36532495
- PMCID: PMC9752027
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1008870
Aeromonas species isolated from aquatic organisms, insects, chicken, and humans in India show similar antimicrobial resistance profiles
Abstract
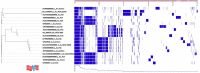
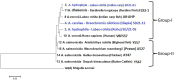
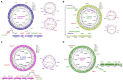
Aeromonas species are Gram-negative bacteria that infect various living organisms and are ubiquitously found in different aquatic environments. In this study, we used whole genome sequencing (WGS) to identify and compare the antimicrobial resistance (AMR) genes, integrons, transposases and plasmids found in Aeromonas hydrophila, Aeromonas caviae and Aeromonas veronii isolated from Indian major carp (Catla catla), Indian carp (Labeo rohita), catfish (Clarias batrachus) and Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) sampled in India. To gain a wider comparison, we included 11 whole genome sequences of Aeromonas spp. from different host species in India deposited in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Our findings show that all 15 Aeromonas sequences examined had multiple AMR genes of which the Ambler classes B, C and D β-lactamase genes were the most dominant. The high similarity of AMR genes in the Aeromonas sequences obtained from different host species point to interspecies transmission of AMR genes. Our findings also show that all Aeromonas sequences examined encoded several multidrug efflux-pump proteins. As for genes linked to mobile genetic elements (MBE), only the class I integrase was detected from two fish isolates, while all transposases detected belonged to the insertion sequence (IS) family. Only seven of the 15 Aeromonas sequences examined had plasmids and none of the plasmids encoded AMR genes. In summary, our findings show that Aeromonas spp. isolated from different host species in India carry multiple AMR genes. Thus, we advocate that the control of AMR caused by Aeromonas spp. in India should be based on a One Health approach.
Keywords: Aeromonas; antimicrobials; beta lactam; integrase; plasmids; resistance; transposase genes.
Copyright © 2022 Dubey, Ager-Wick, Kumar, Karunasagar, Karunasagar, Peng, Evensen, Sørum and Munang’andu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The mobile gene cassette carrying tetracycline resistance genes in Aeromonas veronii strain Ah5S-24 isolated from catfish pond sediments shows similarity with a cassette found in other environmental and foodborne bacteria.Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 15;14:1112941. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1112941. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37007502 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug resistant Aeromonas spp. isolated from zebrafish (Danio rerio): antibiogram, antimicrobial resistance genes and class 1 integron gene cassettes.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2019 May;68(5):370-377. doi: 10.1111/lam.13138. Epub 2019 Mar 19. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30790321
-
Whole genome sequence analysis of Aeromonas spp. isolated from ready-to-eat seafood: antimicrobial resistance and virulence factors.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jun 30;14:1175304. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1175304. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37455746 Free PMC article.
-
An in silico analysis of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes in Aeromonas plasmids.AIMS Microbiol. 2020 Mar 16;6(1):75-91. doi: 10.3934/microbiol.2020005. eCollection 2020. AIMS Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32226916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Newer β-Lactam/β-Lactamase inhibitor for multidrug-resistant gram-negative infections: Challenges, implications and surveillance strategy for India.Indian J Med Microbiol. 2018 Jul-Sep;36(3):334-343. doi: 10.4103/ijmm.IJMM_18_326. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30429384 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytotoxicity and Antimicrobial Resistance of Aeromonas Strains Isolated from Fresh Produce and Irrigation Water.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Mar 3;12(3):511. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12030511. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978377 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiota Dysbiosis in Mytilus chilensis Is Induced by Hypoxia, Leading to Molecular and Functional Consequences.Microorganisms. 2025 Apr 5;13(4):825. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13040825. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40284661 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiological insight into bacterial risk associated with flooded areas of city agglomeration (Wrocław, Poland 2024).Sci Rep. 2025 May 25;15(1):18182. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-03001-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40415099 Free PMC article.
-
Global spread and antimicrobial resistance of Aeromonas hydrophila in aquatic food animals: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 4;15(1):28441. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14498-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40759729 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic resistance profiles of oral flora in hippopotami (Hippopotamus amphibius): implications for treatment of human bite wound infections.One Health Outlook. 2025 Apr 23;7(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s42522-025-00146-8. One Health Outlook. 2025. PMID: 40269996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdelsalam M., Ewiss M. Z., Khalefa H. S., Mahmoud M. A., Elgendy M. Y., Abdel-Moneam D. A. (2021). Coinfections of Aeromonas spp., enterococcus faecalis, and vibrio alginolyticus isolated from farmed Nile tilapia and African catfish in Egypt, with an emphasis on poor water quality. Microb. Pathog. 160:105213. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105213 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abraham T. J., Anwesha R., Julinta R. B., Singha J., Patil P. K. (2017). Efficacy of oxytetracycline and potentiated sulphonamide oral therapies against Aeromonas hydrophila infection in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. J. Coast. Life Med. 5, 371–374. doi: 10.12980/jclm.5.2017j7-89 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

