Study on the physicochemical and flavor characteristics of air frying and deep frying shrimp (crayfish) meat
- PMID: 36532562
- PMCID: PMC9752907
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1022590
Study on the physicochemical and flavor characteristics of air frying and deep frying shrimp (crayfish) meat
Abstract
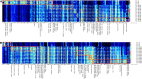
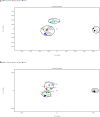
This study aimed to compare the changes in the quality characteristics of air-fried (AF) shrimp meat and deep-fried (DF) shrimp meat at different frying temperatures (160, 170, 180, 190°C). Results showed that compared with DF, the moisture and fat content of air-fried shrimp meat (AFSM) was lower, while the protein content was higher. At the same frying temperature, the fat content of the AFSM was 4.26-6.58 g/100 g lower than that of the deep-fried shrimp meat (DFSM). The smell of the AFSM and DFSM was significantly different from that of the control group. The results of the electronic tongue showed that each of the two frying methods had its flavor profile. Gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (GC-IMS) identified 48 compounds, and the content of volatile compounds detected in AFSM was lower than that in DFSM. Among them, the highest level of volatile compound content was found in the DF-190. E-2-pentenal, 2-heptenal (E), and methyl 2-methyl butanoate were identified only in DFSM. In addition, a total of 16 free amino acids (FAAs) were detected in shrimp meat. As judged by sensory evaluation, the AFSM at 170°C was the most popular among consumers.
Keywords: air frying; deep frying; flavor characteristics; physicochemical properties; shrimps.
Copyright © 2022 Zhou, Shi, Deng, Wang, Qiao, Xiong, Wang, Wu, Shi and Ding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Comparative Studies on the Physicochemical and Volatile Flavour Properties of Traditional Deep Fried and Circulating-Air Fried Hairtail (Trichiurus lepturus).Foods. 2022 Sep 5;11(17):2710. doi: 10.3390/foods11172710. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36076895 Free PMC article.
-
Physicochemical and Volatile Flavor Properties of Fish Skin under Conventional Frying, Air Frying and Vacuum Frying.Molecules. 2023 May 26;28(11):4376. doi: 10.3390/molecules28114376. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37298852 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Different Heat Treatments on the Quality and Flavor Compounds of Black Tibetan Sheep Meat by HS-GC-IMS Coupled with Multivariate Analysis.Molecules. 2022 Dec 25;28(1):165. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010165. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615360 Free PMC article.
-
Deep-fried flavor: characteristics, formation mechanisms, and influencing factors.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020;60(9):1496-1514. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2019.1575792. Epub 2019 Feb 11. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020. PMID: 30740987 Review.
-
A review on the frying process: Methods, models and their mechanism and application in the food industry.Food Res Int. 2023 Oct;172:113176. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113176. Epub 2023 Jun 20. Food Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37689929 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of quantitative marinating on meat quality, biogenic amines, and flavor compounds in crayfish meat.Front Nutr. 2025 Apr 10;12:1573987. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1573987. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40276529 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring of Volatile Compounds of Ready-to-Eat Kiwifruit Using GC-IMS.Foods. 2023 Dec 6;12(24):4394. doi: 10.3390/foods12244394. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38137198 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of changes in sensory, physicochemical properties and microbial metabolic activities of grass carp meat with five thermal processing treatments during refrigerated storage.Food Chem X. 2024 Jul 15;23:101662. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101662. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Food Chem X. 2024. PMID: 39148526 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Analysis between Volatile Compounds and Quality Attributes in Pork Tenderloin in Response to Different Stir-Frying Processes.Foods. 2023 Nov 28;12(23):4299. doi: 10.3390/foods12234299. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38231781 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Communities of Air-Fried Hairtail Fillets during Storage.Foods. 2024 Mar 3;13(5):786. doi: 10.3390/foods13050786. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38472899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bou R, Navas JA, Tres A, Codony R, Guardiola F. Quality assessment of frying fats and fried snacks during continuous deep-fat frying at different large-scale producers. Food Control. (2012) 27:254–67. 10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.03.026 - DOI
-
- Saguy IS, Dana D. Integrated approach to deep fat frying: engineering, nutrition, health, and consumer aspects. J Food Eng. (2003) 56:143–52. 10.1016/S0260-8774(02)00243-1 - DOI
-
- Abd Rahman NA, Abdul Razak SZ, Lokmanalhakim LA, Taip FS, Mustapa Kamal SM. Response surface optimization for hot air-frying technique and its effects on the quality of sweet potato snack. J Food Process Eng. (2017) 40:e12507. 10.1111/jfpe.12507 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

